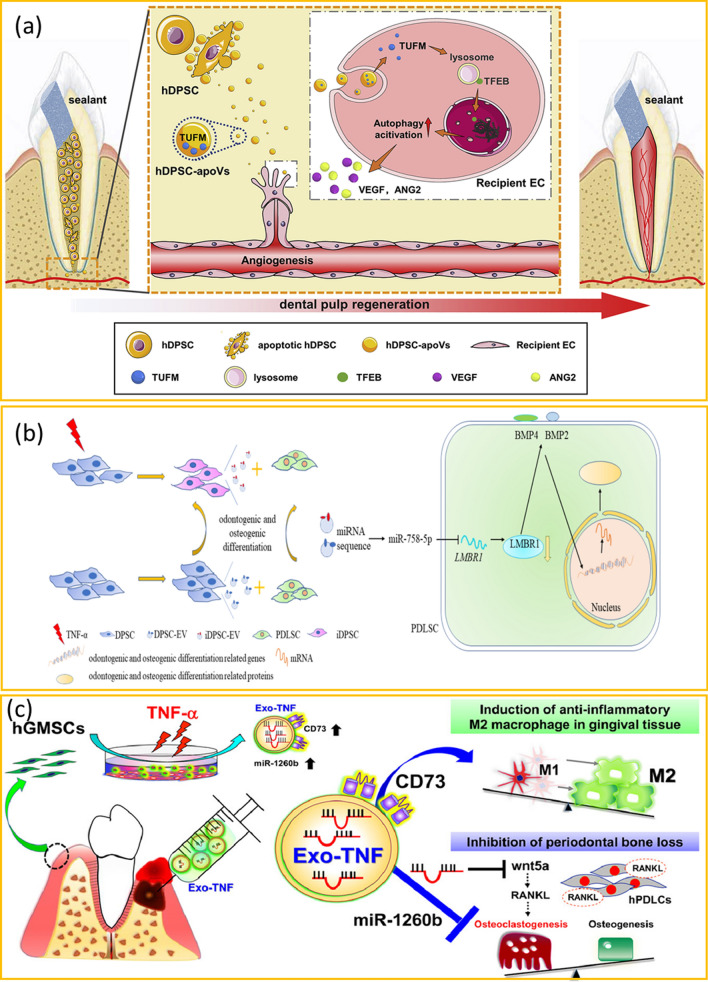
Fig. 6.
The mode of action of extracellular vesicles in promoting different dental tissue regeneration. a EVs derived from DPSCs specifically activate endogenous EC autophagy by transferring TUFM, thereby causing angiogenesis. The acceleration of vascular reconstruction promotes dental pulp regeneration. This figure is adapted and is freely accessible from reference [81], Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0). b EVs derived from DPSCs under an inflammatory microenvironment participate in the regulating of odontogenic and osteogenic differentiation by miR-758-5p/LMBR1/BMP2/4 axis. This figure is adapted and is freely accessible from reference [99], Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0). c EVs derived from GMSCs under inflammation microenvironment enhance M2-type macrophage polarization and prevent periodontal bone loss. This figure is adapted and is freely accessible from reference [39], Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0). Abbreviations: EC, endothelial cells; hDPSC, human dental pulp stem cells; TUFM, Tu translation elongation factor, mitochondrial; TFEB, transcription factor EB; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; ANG2, angiotensin 2; hDPSC-apoVs, apoptotic vesicles from human dental pulp stem cells; BMP, bone morphogenetic protein; LMBR1, limb development membrane protein 1; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor α; DPSC-EV, EVs from dental pulp stem cells; iDPSC-EVs, EVs from dental pulp stem cells under inflammatory environment; PDLSC, periodontal ligament stem cells