Abstract
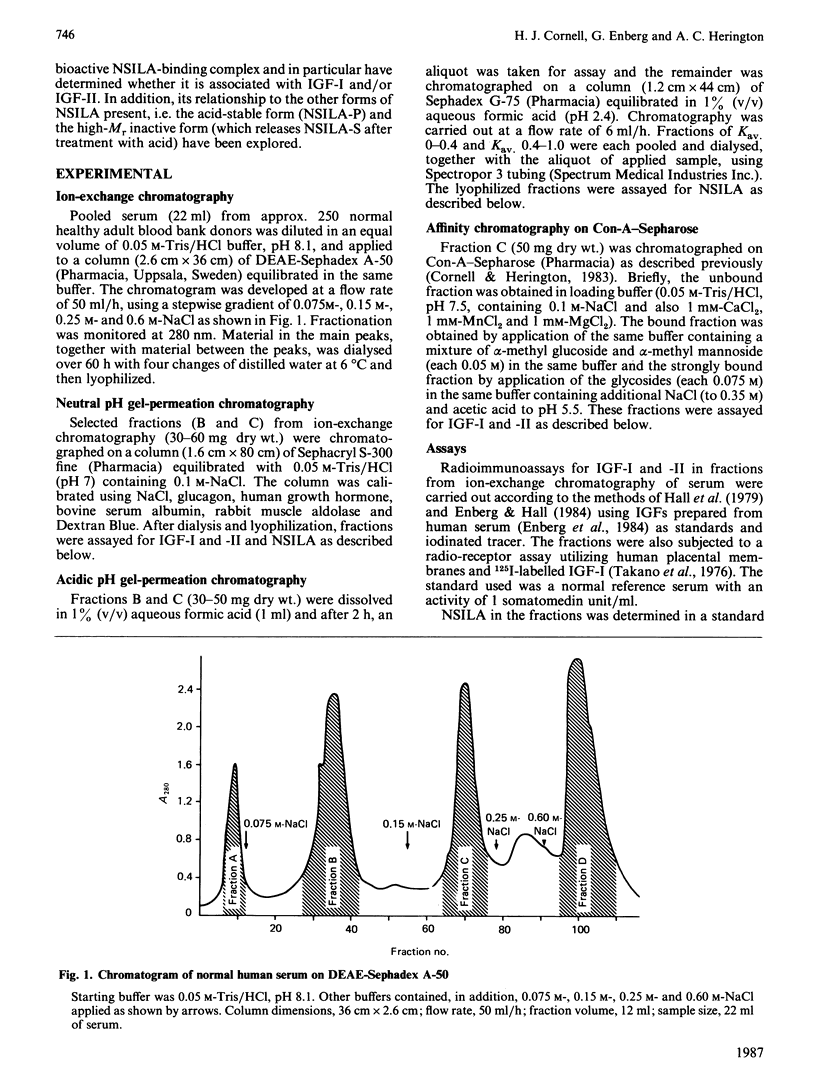
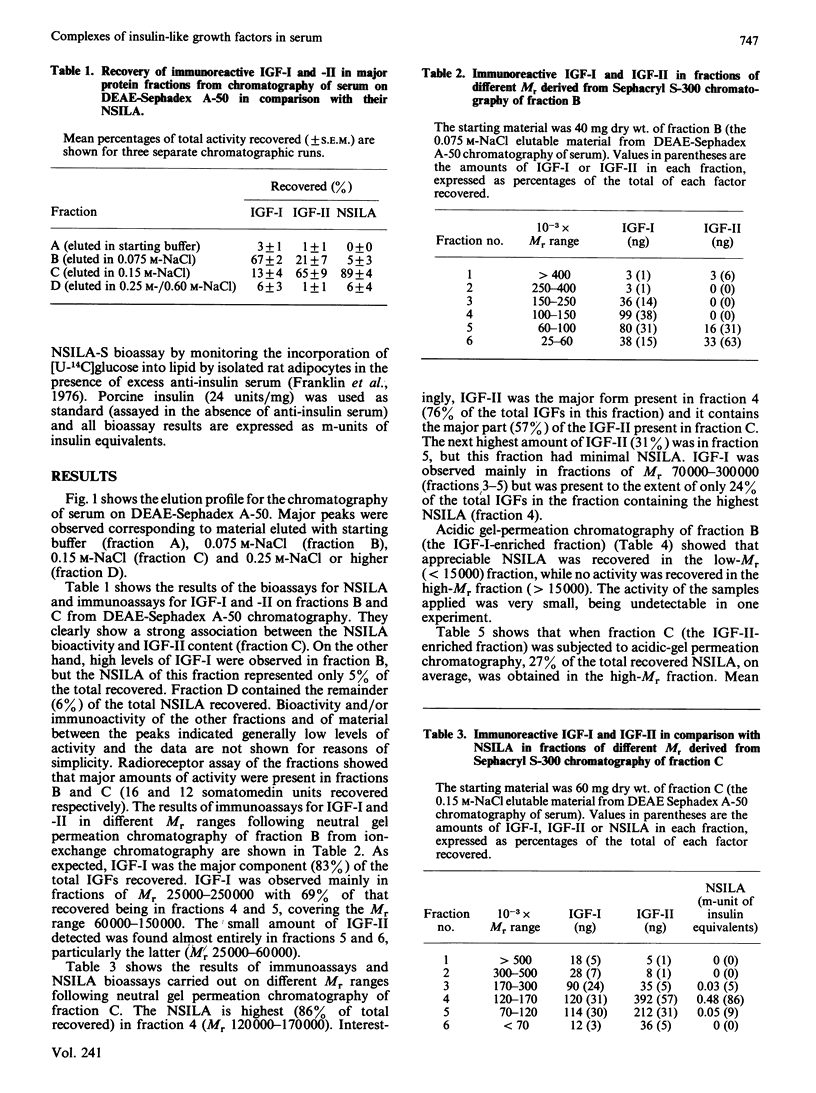
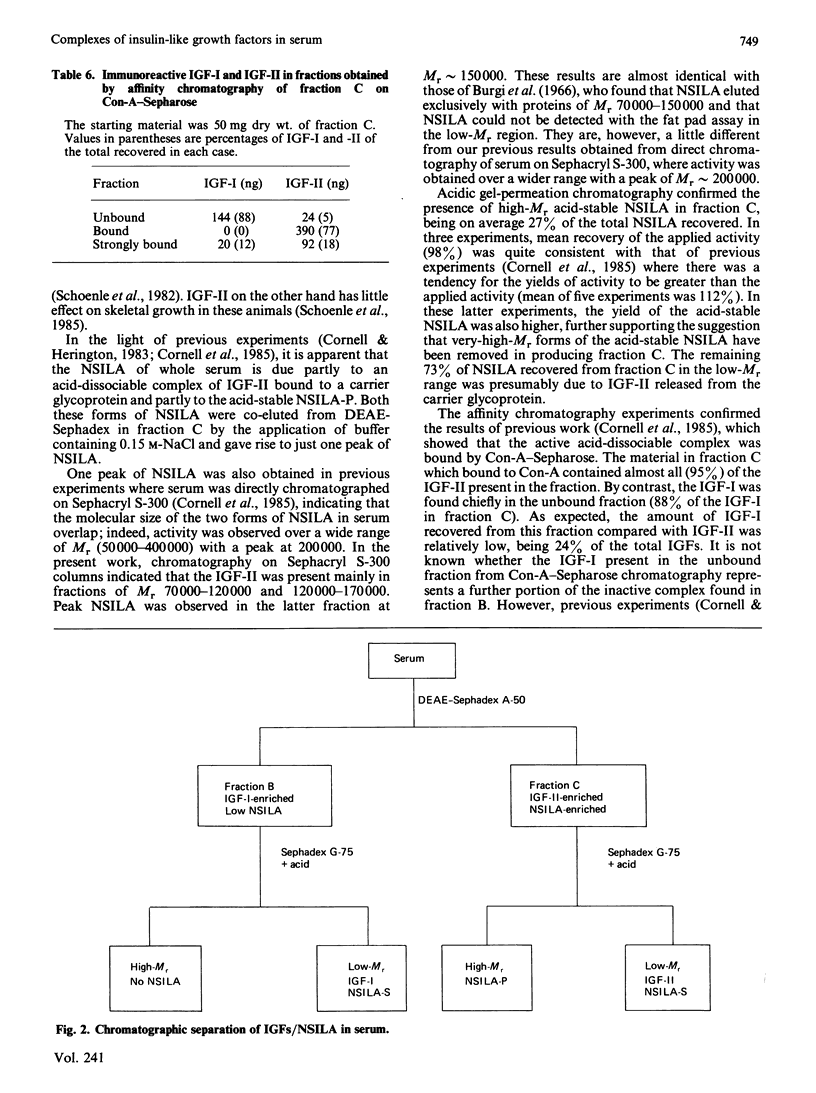
Ion-exchange chromatography of serum on DEAE-Sephadex A-50 using a stepwise NaCl gradient showed that complexes enriched with insulin-like growth factors I and II (IGF-I and IGF-II) could be preferentially eluted. A fraction eluted with 0.075 M-NaCl preferentially contained immunoreactive IGF-I with peak levels appearing in fractions of Mr approx. 110,000. The IGF-I-binding protein complex itself had low bioactivity as measured in a non-suppressible insulin-like (NSILA) bioassay. On conversion to free IGF-I by gel-permeation chromatography on Sephadex G-75 in 1% formic acid, however, the IGF-I did express its intrinsic NSILA bioactivity. In contrast, an IGF-II-enriched complex was eluted from the DEAE-Sephadex with 0.15 M-NaCl. Practically all of the recovered NSILA of the original serum was present in this fraction, in the Mr range 70,000-300,000 with a peak of 150,000. Chromatography on Sephadex G-75 in 1% formic acid separated this high-Mr NSILA into low-Mr (less than 15000) IGF-II and high-Mr acid-stable NSILA-P. The high-Mr IGF-II complex bound to concanavalin A-Sepharose, suggesting that it was a glycoprotein. The results confirm previous reports that a large portion of the NSILA of whole serum can be accounted for by a biologically active acid-dissociable complex. These data show for the first time that this active complex consists of an IGF-II-preferring binding protein. In direct contrast, the IGF-I-preferring complex does not express NSILA bioactivity until the IGF-I is liberated through acidification. The presence of a metabolically active IGF-II complex in serum raises questions as to its possible biological role in the adult.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams S. O., Nissley S. P., Handwerger S., Rechler M. M. Developmental patterns of insulin-like growth factor-I and -II synthesis and regulation in rat fibroblasts. Nature. 1983 Mar 10;302(5904):150–153. doi: 10.1038/302150a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bürgi H., Müller W. A., Humbel R. E., Labhart A., Froesch E. R. Non-suppressible insulin-like activity of human serum. I. Physicochemical properties, extraction and partial purification. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jun 29;121(2):349–359. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90124-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatelain P. G., Van Wyk J., Copeland K. C., Blethen S. L., Underwood L. E. Effect of in vitro action of serum proteases or exposure to acid on measurable immunoreactive somatomedin-C in serum. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 Feb;56(2):376–383. doi: 10.1210/jcem-56-2-376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockerill P. N., Cornell H. J., Herington A. C. Partial purification of low molecular weight non-suppressible insulin-like activity from human plasma: demonstration of the presence of multiple forms. J Endocrinol. 1980 May;85(2):266–277. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0850267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornell H. J., Bistrin M., Herington A. C. Differentiation between carrier-bound forms of non-suppressible insulin-like activity (NSILA) in serum. Int J Biochem. 1985;17(9):1003–1008. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(85)90246-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornell H. J., Herington A. C. Evidence for a biologically active, carrier-bound form of non-suppressible insulin-like activity (NSILA) in human serum. Int J Biochem. 1983;15(4):553–558. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(83)90130-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enberg G., Carlquist M., Jörnvall H., Hall K. The characterization of somatomedin A, isolated by microcomputer-controlled chromatography, reveals an apparent identity to insulin-like growth factor 1. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Aug 15;143(1):117–124. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08349.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enberg G., Hall K. Immunoreactive IGF-II in serum of healthy subjects and patients with growth hormone disturbances and uraemia. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1984 Oct;107(2):164–170. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1070164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin R. C., Rennie G. C., Burger H. G., Cameron D. P. A bioassay for NSILA-S in individual serum samples and its relationship to somatotropin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1976 Nov;43(5):1164–1169. doi: 10.1210/jcem-43-5-1164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furlanetto R. W. The somatomedin C binding protein: evidence for a heterologous subunit structure. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1980 Jul;51(1):12–19. doi: 10.1210/jcem-51-1-12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall K., Brandt J., Enberg G., Fryklund L. Immunoreactive somatomedin A in human serum. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1979 Feb;48(2):271–278. doi: 10.1210/jcem-48-2-271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herington A. C., Cornell H. J., Kuffer A. D. Recent advances in the biochemistry and physiology of the insulin-like growth factor/somatomedin family. Int J Biochem. 1983;15(10):1201–1210. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(83)90208-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herington A. C., Kuffer A. D. Identification of a specific inhibitor of nonsuppressible insulin-like activity in a partially purified human serum fraction. Endocrinology. 1981 Nov;109(5):1634–1640. doi: 10.1210/endo-109-5-1634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herington A. C., Kuffer A. D. Insulin-like growth factor characteristics of an acidic non-suppressible insulin-like activity. Biochem J. 1984 Oct 1;223(1):89–96. doi: 10.1042/bj2230089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hintz R. L., Liu F. Demonstration of specific plasma protein binding sites for somatomedin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1977 Nov;45(5):988–995. doi: 10.1210/jcem-45-5-988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hintz R. L., Liu F., Rosenfeld R. G., Kemp S. F. Plasma somatomedin-binding proteins in hypopituitarism: changes during growth hormone therapy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1981 Jul;53(1):100–104. doi: 10.1210/jcem-53-1-100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann U., Zapf J., Torretti B., Froesch E. R. Demonstration of a specific serum carrier protein of nonsuppressible insulin-like activity in vivo. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1977 Jan;44(1):160–166. doi: 10.1210/jcem-44-1-160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klapper D. G., Svoboda M. E., Van Wyk J. J. Sequence analysis of somatomedin-C: confirmation of identity with insulin-like growth factor I. Endocrinology. 1983 Jun;112(6):2215–2217. doi: 10.1210/endo-112-6-2215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuli C., Zapf J., Froesch E. R. NSILA-carrier protein abolishes the action of nonsuppressible insulin-like activity (NSILA-S) on perfused rat heart. Diabetologia. 1978 Apr;14(4):255–259. doi: 10.1007/BF01219425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris D. H., Schalch D. S. Structure of somatomedin-binding protein: alkaline pH-induced dissociation of an acid-stable, 60,000 molecular weight complex into smaller components. Endocrinology. 1982 Sep;111(3):801–805. doi: 10.1210/endo-111-3-801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips L. S., Fusco A. C., Unterman T. G., del Greco F. Somatomedin inhibitor in uremia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984 Oct;59(4):764–772. doi: 10.1210/jcem-59-4-764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poffenbarger P. L. The purification and partial characterization of an insulin-like protein from human serum. J Clin Invest. 1975 Dec;56(6):1455–1463. doi: 10.1172/JCI108226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinderknecht E., Humbel R. E. Polypeptides with nonsuppressible insulin-like and cell-growth promoting activities in human serum: isolation, chemical characterization, and some biological properties of forms I and II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2365–2369. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenle E., Zapf J., Hauri C., Steiner T., Froesch E. R. Comparison of in vivo effects of insulin-like growth factors I and II and of growth hormone in hypophysectomized rats. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1985 Feb;108(2):167–174. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1080167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenle E., Zapf J., Humbel R. E., Froesch E. R. Insulin-like growth factor I stimulates growth in hypophysectomized rats. Nature. 1982 Mar 18;296(5854):252–253. doi: 10.1038/296252a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. L. Somatomedin carrier proteins. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1984 Feb;34(2):83–89. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(84)90058-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takano K., Hall K., Ritzén M., Iselius L., Sievertsson H. Somatomedin A in human serum, determined by radioreceptor assay. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1976 Jul;82(3):449–459. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0820449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkins J. R., D'Ercole A. J. Affinity-labeled plasma somatomedin-C/insulinlike growth factor I binding proteins. Evidence of growth hormone dependence and subunit structure. J Clin Invest. 1985 Apr;75(4):1350–1358. doi: 10.1172/JCI111836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Jagars G., Sand I., Froesch E. R. Evidence for the existence in human serum of large molecular weight nonsuppressible insulin-like activity (NSILA) different from the small molecular weight forms. FEBS Lett. 1978 Jun 1;90(1):135–140. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80315-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Schoenle E., Jagars G., Sand I., Grunwald J., Froesch E. R. Inhibition of the action of nonsuppressible insulin-like activity on isolated rat fat cells by binding to its carrier protein. J Clin Invest. 1979 May;63(5):1077–1084. doi: 10.1172/JCI109377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Waldvogel M., Froesch E. R. Binding of nonsuppressible insulinlike activity to human serum. Evidence for a carrier protein. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Jun;168(2):638–645. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90296-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Walter H., Froesch E. R. Radioimmunological determination of insulinlike growth factors I and II in normal subjects and in patients with growth disorders and extrapancreatic tumor hypoglycemia. J Clin Invest. 1981 Nov;68(5):1321–1330. doi: 10.1172/JCI110379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


