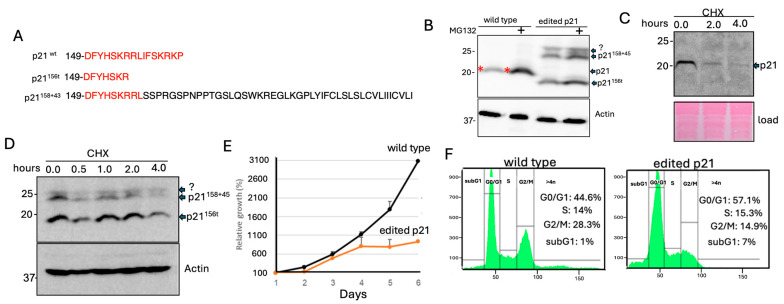
Figure 4.
Analysis of p21 edited HEK293 cells. (A) Protein sequence of wild type p21 and the edited p21 in HEK293 cells using CRISPR technology. Two alleles were edited differently: p21156t is a truncated mutant missing the last 9 amino acids of the C-terminus, including the RLIF box, while p21158+43 is a frameshift mutant where the C-terminus 9 amino acids are replaced by a new reading frame of 43 amino acids. The red letters in the sequence represent the wild-type p21 sequence. (B) p21 expression in the edited cells was analyzed in the absence or presence of MG132 for 4 h, a proteasome inhibitor. The asterisk (*) indicates the position of wild-type p21. The band labeled with a question mark (?) represents an unidentified one. (C) p21 protein decay was assessed using cycloheximide (CHX), a translation inhibitor, for the indicated time points. (D) Decay of p21 in the edited HEK293 clone, as described in panel (A), was examined using CHX treatment as outlined in panel. The band labeled with a question mark (?) represents an unidentified one. (C). (E) Comparison of relative growth between control HEK293 cells and the HEK293 p21-edited clone. (F) Cell cycle distribution of the cells was analyzed using FACS.