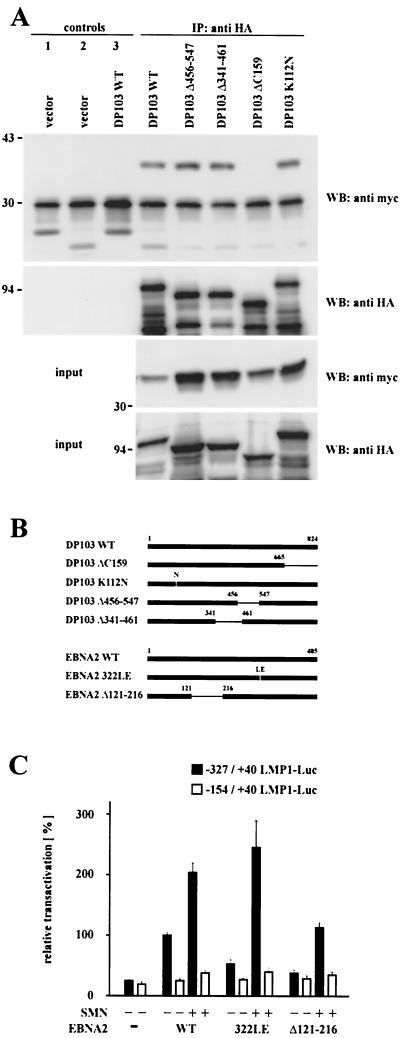
FIG. 4.
EBNA2-mediated transactivation of the LMP1 promoter involves binding of EBNA2 to DP103. (A) Mapping of the SMN binding site on DP103. 293GP cells were transfected with pSG5 constructs encoding HA-tagged DP103 mutants and WT myc-tagged SMN, as indicated. Cell extracts were immunoprecipitated with anti-HA MAb 3F10 (IP: anti HA and control 2) or irrelevant MAb 9C2 (controls 1 and 3) and analyzed by SDS–10% PAGE and Western blotting. Precipitated HA-tagged DP103 mutants were detected by using anti-HA MAb 3F10 (WB: anti HA), coprecipitated myc-tagged WT SMN by using anti-myc MAb 9E10 (WB: anti myc). Panels designated input represent ca. 10% of unprecipitated extracts. The positions of the molecular mass markers (in kilodaltons) are indicated on the left side of each panel. Deletion of aa 665 to 824 of DP103 (ΔC159) abolished coprecipitation of myc-tagged SMN. (B) Schematic representation of the DP103 and EBNA2 mutants tested. (C) Coexpression of SMN rescued impaired transactivation of the −327/+40 LMP1 promoter luciferase construct by the DP103 binding-deficient mutant EBNA2 Δ121-216 and the RBPJκ binding-deficient mutant EBNA2 322LE. Assays were performed as described for Fig. 1B. Graphs represent the mean values of three independent experiments performed in duplicate (±SEM).