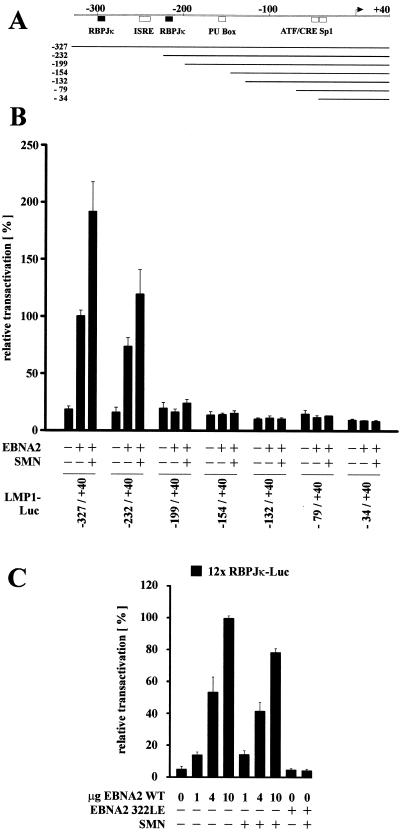
FIG. 5.
The presence of RBPJκ is essential but not sufficient for coactivation by EBNA2 and SMN. (A) Schematic map of positions −327 to +40 of the LMP1 promoter and the different luciferase constructs tested. Shaded boxes represent the positions of cellular transcription factor binding sites, and black boxes represent the positions RBPJκ binding sites relative to the transcription start site (arrow). (B) Deletion mutants of the LMP1 promoter were tested for responsiveness to EBNA2 and coexpressed HA-tagged SMN in BJAB cells, as indicated. Deletion of the RBPJκ binding sites abolished EBNA2 transactivation and coactivation by SMN. (C) No coactivation of a multimerized RBPJκ site by SMN and increasing amounts of WT EBNA2 (1, 4, and 10 μg) or by SMN and RBPJκ binding-deficient EBNA2 322LE. (B and C) Assays were performed as described for Fig. 1B. Graphs represent the mean values of three independent experiments performed in duplicate (±SEM).