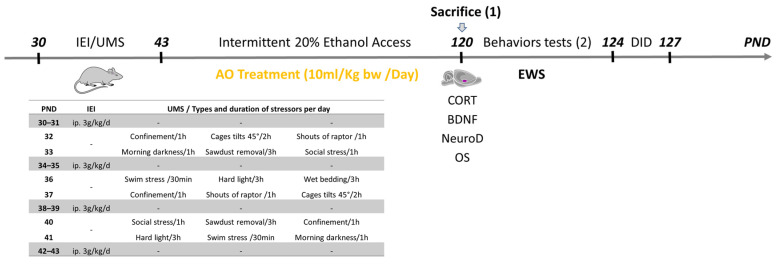
Figure 4.
Experimental timeline and daily schedules for the intermittent ethanol intoxications (IEI) and the unpredictable mild stress (UMS). From post-natal day (PND) 30 to PND 43, IEI animals received a single daily intraperitoneal (ip) administration of ethanol (3 g/kg, 20% ethanol w/v) in the AM on a 2-days-on/2-days-off schedule and Ctrl subjects received comparable volumes of 0.9% saline. On alternate days, the rats were submitted to UMS protocol. The home-cage voluntary intermittent 20% ethanol consumption was measured on a two-bottle choice procedure (from PND 44 to PND 120). During the same period, the rats were treated daily by intragastric gavage with Argan oil (AO, 15 mL/kg–bw). Next, plasma corticosterone (CORT) levels were measured from tail bloods samples in all rats during the last day of AO treatment (between 6:00 p.m. and 7:00 p.m.). One day later, separate groups of each experimentally conditioned rats were used to measure ethanol withdrawal signs (EWS) and binge-like drinking (on the drinking in the dark paradigm (DID)) (2), or were euthanized for histochemical and the biochemical analyses, to measure the neurodegeneration (NeuroD) levels, the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels and the oxidative stress (OS) in the amygdala (1).