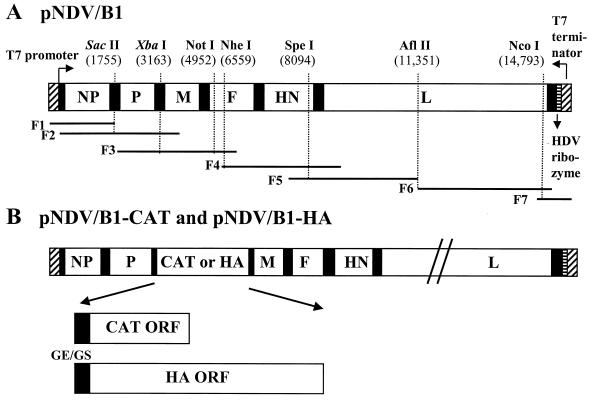
FIG. 1.
Schematic representation of pNDV/B1, pNDV/B1-CAT, and pNDV/B1-HA cDNA constructs. (A) pNDV/B1 was generated by seven PCR fragments spanning the following nucleotide positions: F1, T7 promoter, nt 1755 (SacII); F2, nt 1 to 3321; F3, nt 1755 (SacII) to 6580; F4, nt 6151 to 10,210; F5, nt 7381 to 11,351; F6, nt 11,351 to 14,995; and F7, nt 14,701 to 15,186. These sequences were followed by the hepatitis delta virus (HDV) ribozyme and the T7 terminator. The cDNA fragments were joined at shared restriction sites and assembled in plasmid pSL1180 (Amersham Pharmacia Biotech). SacII and XbaI are shown in italics to indicate that they are genomic tag sequences. (B) The pNDV/B1-CAT and pNDV/B1-HA constructs were made by inserting the CAT and influenza virus A/WSN/33 HA open reading frames (ORF), respectively, into the unique XbaI cloning site (nt 3163) located between the P and M genes of the pNDV/B1 clone. The inserted gene contains the gene end (GE; 5′-TTAGAAAAAA-3′), intercistronic nucleotide (T), and the gene start sequence (GS; 5′-ACGGGTAGAA-3′). In addition, seven nucleotides (5′-CGCCACC-3′) were inserted upstream of the initiation site to introduce an optimal Kozak sequence (13). In the case of pNDV/B1-HA, the gene start sequence is followed by the 5′ untranslated region (26 nt) of the HA gene.