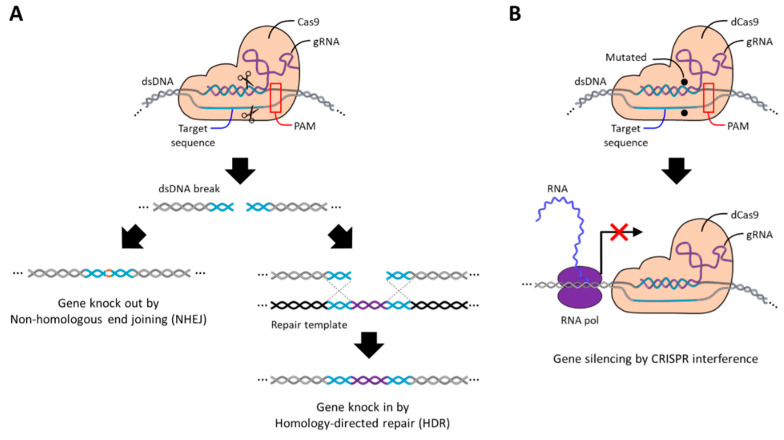
Figure 8.
Schematic images of the CRISPR Cas9 and CRISPR dCas9 systems. (A) Schematic image of CRISPR Cas9 genome editing mechanism. The endonuclease domains of Cas9 (RuvC and HNH) cleave the target sequence after hybridization, and the cut DNA is repaired by NHEJ or HDR, which results in gene disruption or replacement. (B) Schematic image of CRISPR dCas9 gene-silencing mechanism. Mutations in the nuclease domain of dCas9 (D10A and H840A) render it unable to cleave the target sequence after hybridization and interfere with the RNA transcription process through steric hindrance.