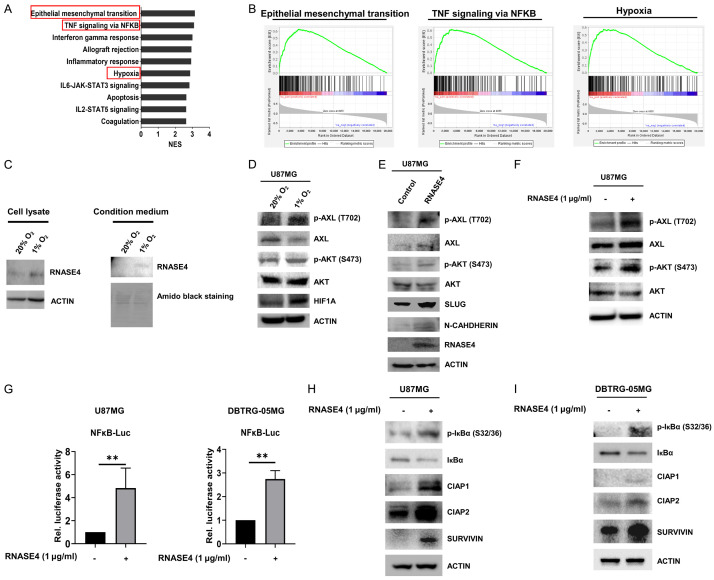
Figure 5.
Hypoxia-induced RNASE4 expression activates AXL/AKT and NF-κB/cIAP1/cIAP2/SURVIVIN signaling in GBM. A, B. GSEA was conducted to reveal the correlation of RNASE4 expression to potential biological pathways. The enrichment plots indicated positive correlation with epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), TNF signaling via NF-κB and hypoxia signatures in TCGA GBM cohort. C. RNASE4 expressions in the cell lysates and conditioned medium of U87MG cells under normoxia and hypoxia conditions were assessed using Western blot analysis. ACTIN served as the internal control for cellular lysates, while Amido Black staining of total secreted proteins was used as the loading control for proteins in the conditioned medium. D. Expression levels of the indicated proteins in U87MG cells cultured under normoxia and hypoxia for 16 hours were assessed by Western blot analysis. E. In addition to the unphosphorylated and phosphorylated levels of AXL and AKT, the protein expressions of EMT markers, including SLUG and N-CADHERIN, in RNASE4-overexpressing U87MG cells were assessed by Western blotting. F. Expressions of unphosphorylated and phosphorylated AXL and AKT in U87MG cells treated with recombinant human RNASE4 protein (hRNASE4) were detected using Western blotting. G. The impact of RNASE4 on NF-κB activation was evaluated by transfecting U87MG and DBTRG-05MG cells with the luciferase reporter construct containing NF-κB-responsive elements. Cells were treated with either vehicle or recombinant human RNASE4 for 16 hours before harvest for reporter activity analysis. Data are presented as mean ± SEM of three independent experiments (**P<0.01). H, I. U87MG and DBTRG-05MG cells treated with recombinant human RNASE4 for 16 hours were subjected to immunoblotting using antibodies specific for phosphorylated IκBα at serine residues 32 and 36 (S32 and S36), unphosphorylated IκBα, cIAP1, cIAP2, and SURVIVIN. ACTIN was used as the loading control.