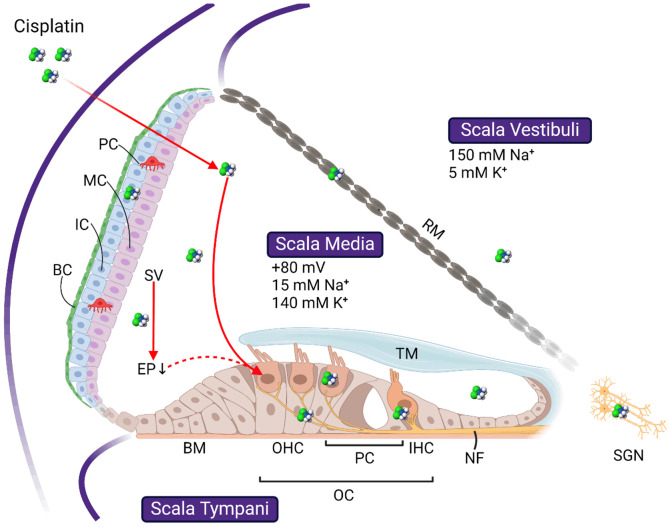
Figure 1.
Schematic image showing the basic cochlear structures and the targets of cisplatin ototoxicity. Cochlear duct forms three scalae, scala vestibuli, scala media, and scala tympani, separated by the basilar membrane (BM) and Reissner’s membrane (RM), respectively. Cells affected by cisplatin include the outer hair cells (OHC) and inner hair cells (IHC) in the organ of Corti (OC), basal cells (BC), intermedial cells (IC), and marginal cells (MC) in the stria vascularis (SV), and the spiral ganglion neurons (SGN) in the modiolus. Whether OHC loss is initiated directly through cisplatin uptake or indirectly through the drop of endocochlear potential (EP) following SV damage is still debating. Refer to the text for more details. TM: tectorial membrane; RM: Reissner’s membrane. All images are created with BioRender.com.