Figure 4. Novelty perturbs the representations of familiar stimuli and their propagation along the visual cortical hierarchy.
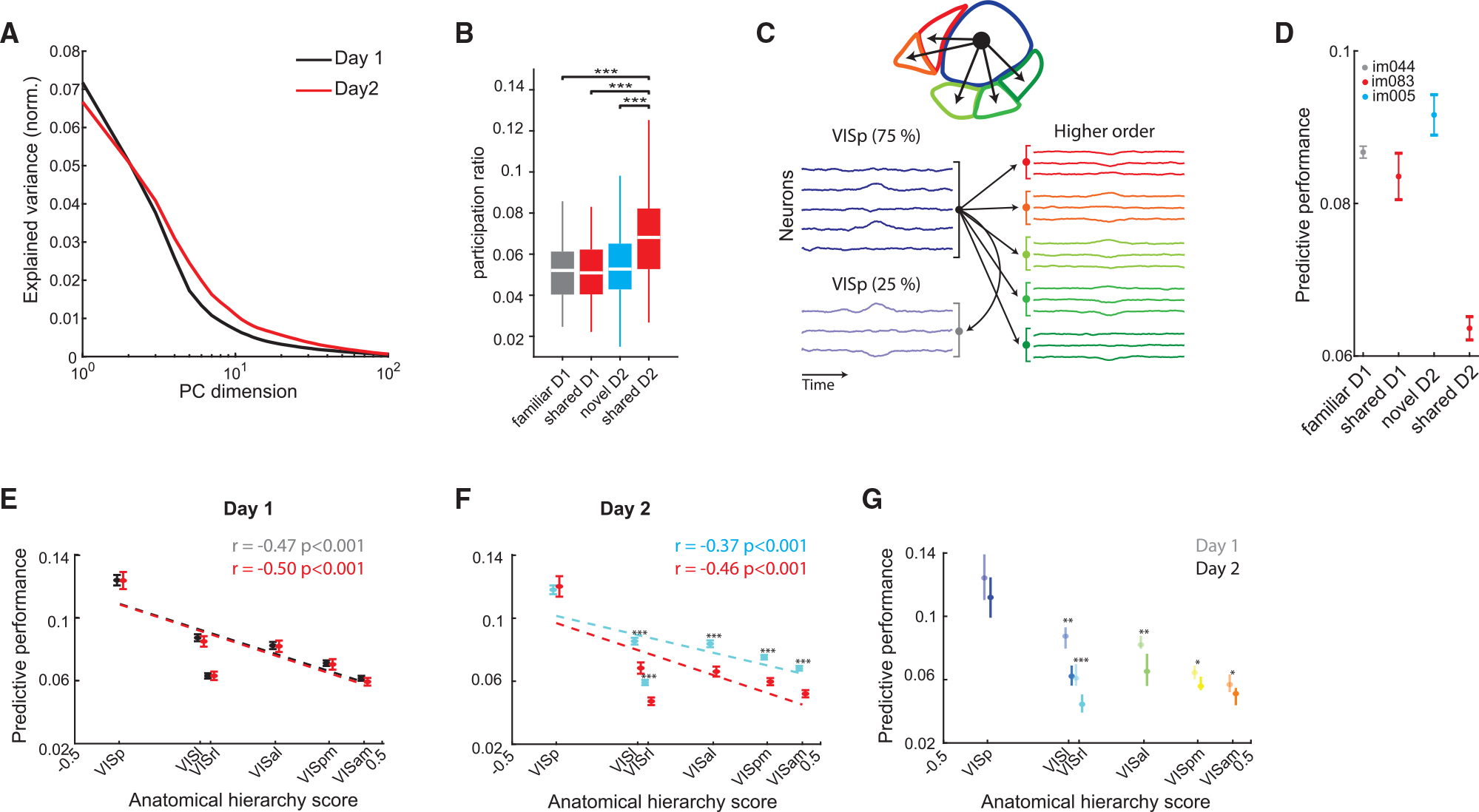
(A) Example eigenspectra of responses to shared stimuli on day 1 (black) and day 2 (red).
(B) Distribution of participation ratio quantifying the intrinsic dimensionality of visual cortex population activity in response to the different image types(***p < 0.001, Kruskal-Wallis with Tukey-Kramer post hoc tests).
(C) Illustration of the cross-validated ridge regression model used VISp activity to predict the activity in higher-order visual areas or a withheld VISp subpopulation.
(D) Performance (mean ± SEM across folds) of a cross-validated ridge regression model trained to predict VISam activity from VISp activity in an example mouse for a familiar image and a novel image on day 1 and 2, respectively, as well as the same shared image on both days. Note the decreased performance for the shared image on day 2.</p/>(E) Predictive performance (mean ± SEM) for all higher-order visual areas, as well as a held-out VISp population for familiar (gray) and shared (red) images on day 1 (familiar/shared differences are not significant; n = 26–30 sessions per area). Dotted lines, linear regression lines.
(F) Same as (E), for novel (cyan) and shared (red) images on day 2. Predictive performance of activity during the presentation of shared images was significantly lower than that of novel images in all higher-order visual areas, but not in VISp (p < 0.001, Wilcoxon rank-sum test; n = 31–33 sessions per area).
(G) Comparison of predictive performance (median ± 95% confidence intervals) for shared images on day 1 (opaque colors) and day 2 (bright colors) for the different visual cortical areas, sorted by their anatomical hierarchy score (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, Wilcoxon rank-sum test with Bonferroni-Holm corrections).
