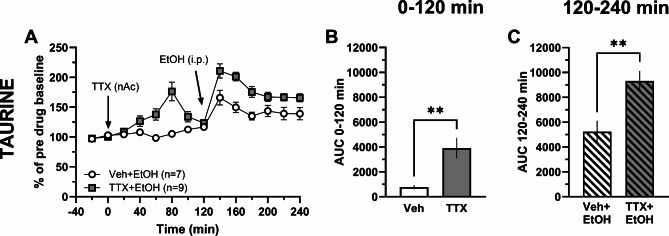
Fig. 2.
Tetrodotoxin does not prevent ethanol from increasing taurine in the nAc. Time-course graphs of extracellular levels of A taurine in the nAc after TTX (1 µM, reversed microdialysis) and ethanol (2.5 g/kg i.p.) administration. Area under the curve of B taurine levels during local perfusion with vehicle (Ringer’s solution) or TTX during 0–120 min demonstrates that TTX increases extracellular taurine levels compared to Ringer-treated controls. Area under the curve of C taurine levels during local perfusion with vehicle or TTX and the addition of ethanol (i.p.) during 120–240 min demonstrates that ethanol further elevates extracellular taurine levels in TTX-perfused animals. All data are presented as mean ± SEM. **p < 0.01. AUC = area under the curve, EtOH = ethanol, nAc = nucleus accumbens, TTX = tetrodotoxin, Veh = vehicle.