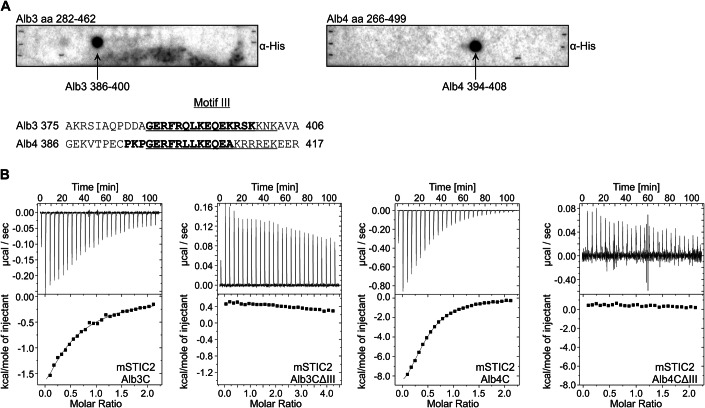
Figure 5. The conserved C-terminal Motif III of Alb3 and Alb4 is the primary interaction site for STIC2.
(A) The interaction of His-STIC2 with the C-terminal regions of Alb3 (aa 282–462, left side) and Alb4 (aa 266–499, right side) was analyzed using pepspot-labeled nitrocellulose membranes. Recombinant His-STIC2 was incubated in a final concentration of 5 µg/ml with the pepspot membranes. Bound His-STIC2 was detected with antisera directed against the His-tag. Detected spots correspond to amino acids 386–400 of Alb3 and amino acids 394–408 of Alb4. These residues are indicated in bold in an alignment of a C-terminal region of Alb3 and Alb4 comprising the conserved Motif III (underlined). (B) Representative measurements of isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) to determine binding affinities for the interaction of STIC2 with the C-terminal regions of Alb3 and Alb4. Left panels: 1.5 mM His-STIC2 was titrated into 0.15 mM of Alb3C-His or Alb3CΔIII-His. Right panels: 1 mM His-STIC2 was titrated into 0.1 mM Alb4C-His or Alb4CΔIII-His solutions. The resulting changes in heating power were recorded (top panels). After integration, the resulting enthalpy changes are plotted versus the molar ratio of STIC2 and the indicated binding partners (bottom panels). The titration isotherms resulted in a Kd of 150 ± 30 µM for the STIC2/Alb3C interaction and a Kd of 17 ± 4 µM for the STIC2/Alb4C interaction. No binding was detected for STIC2/Alb3CΔIII and STIC2/Alb4CΔIII. Data were calculated from two to five independent experiments. Source data are available online for this figure.