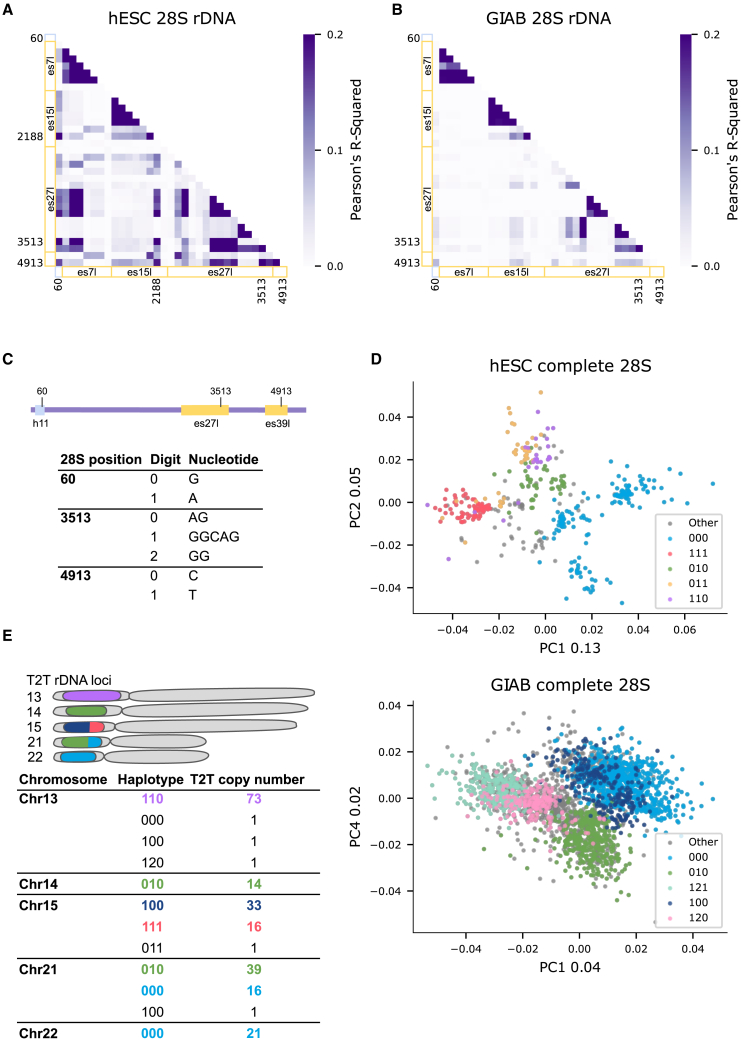
Figure 3.
28S subtypes found by haplotype analysis
(A) Correlation coefficient (Pearson’s r2) heatmap between positions across H7-hESC 28S rDNA with variant frequency >10%. x axis and y axis are annotated by regions. Helix regions are annotated by light blue, and ES regions are annotated by yellow. Individual positions with higher r2 between regions are also indicated.
(B) Same as (A) for the Genome In A Bottle (GIAB) dataset.
(C) Haplotype digit code to variant sequence conversion at the three positions with higher r2 in (A) and (B).
(D) Bray-Curtis principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) of 386 H7-hESC 28S rDNA sequences (upper panel) and 386 28S rDNA sequences from each GIAB sample (lower panel). Each dot is a complete 28S rDNA sequence with similarity between sequences measured on 6-mers. The colors correspond to coloring an rDNA sequence by its 3-position haplotype described in (C). Numbers in the x and y labels represent the PCoA explained variance.
(E) Telomere-to-telomere (T2T) haplotype distribution across the five acrocentric chromosomes. The rDNA acrocentric arms are presented in a schematic cartoon with proportions of rDNA haplotypes in different colors as found in the matching table below. Haplotypes match the 3-position haplotypes in (C). We indicate the rDNA copy number of each haplotype in every chromosome.