Figure 1.
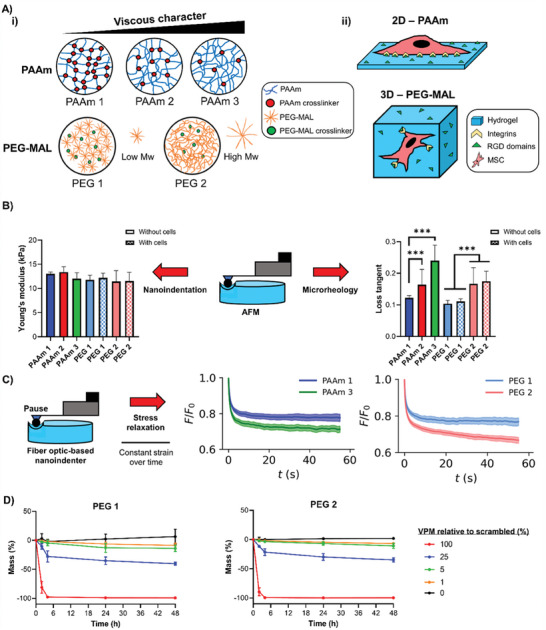
PAAm and PEG‐MAL isoelastic hydrogels with tuneable viscous component. A‐i) Representation of PAAm and PEG‐MAL polymer:crosslinking ratios and molecular weight differences within hydrogels and the influence on their loss tangent and ii) sketch of 2D/3D dimensionality of each hydrogel system as cell culture platforms. B) AFM microscale measurements of PAAm and PEG‐MAL (crosslinked with 1% VPM relative to scrambled) hydrogels using nanoindentation for Young's modulus (left) and microrheology for loss tangent (right); PEG‐MAL hydrogels were measured without cells and in the presence of encapsulated cells; n = 50–100. C) Stress relaxation measurements of hydrogels using a fiber‐optic‐based nanoindenter with pause step for PAAm (left) and PEG‐MAL (crosslinked with 1% VPM relative to scrambled) (right) hydrogels, n = 100. D) Biodegradability of PEG‐MAL hydrogels crosslinked with different degrees of VPM (relative to scrambled VPM) represented by mass loss over 48 h in the presence of collagenase D for PEG 1 (left) and PEG 2 (right), n = 3. For all figures, data are represented as mean ± standard deviation and differences are considered significant for p ≤ 0.05 using one‐way ANOVAs for multiple comparisons (*** p ≤ 0.001).
