Abstract
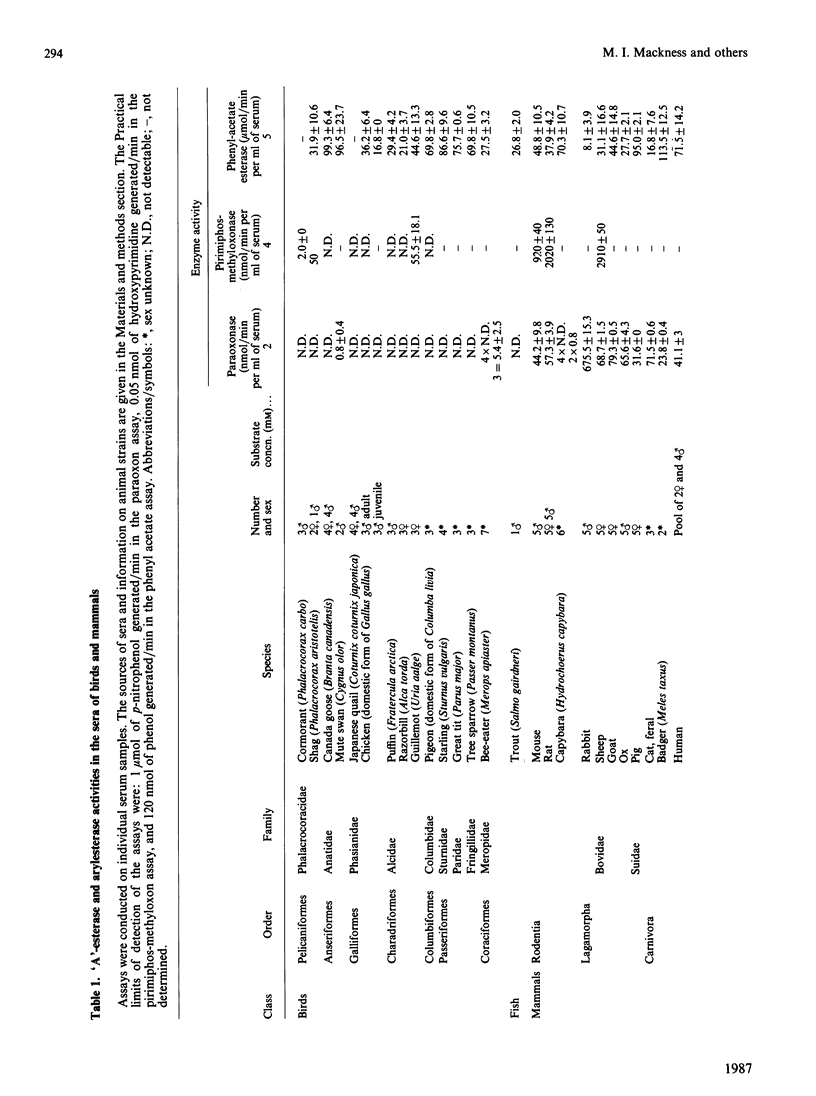
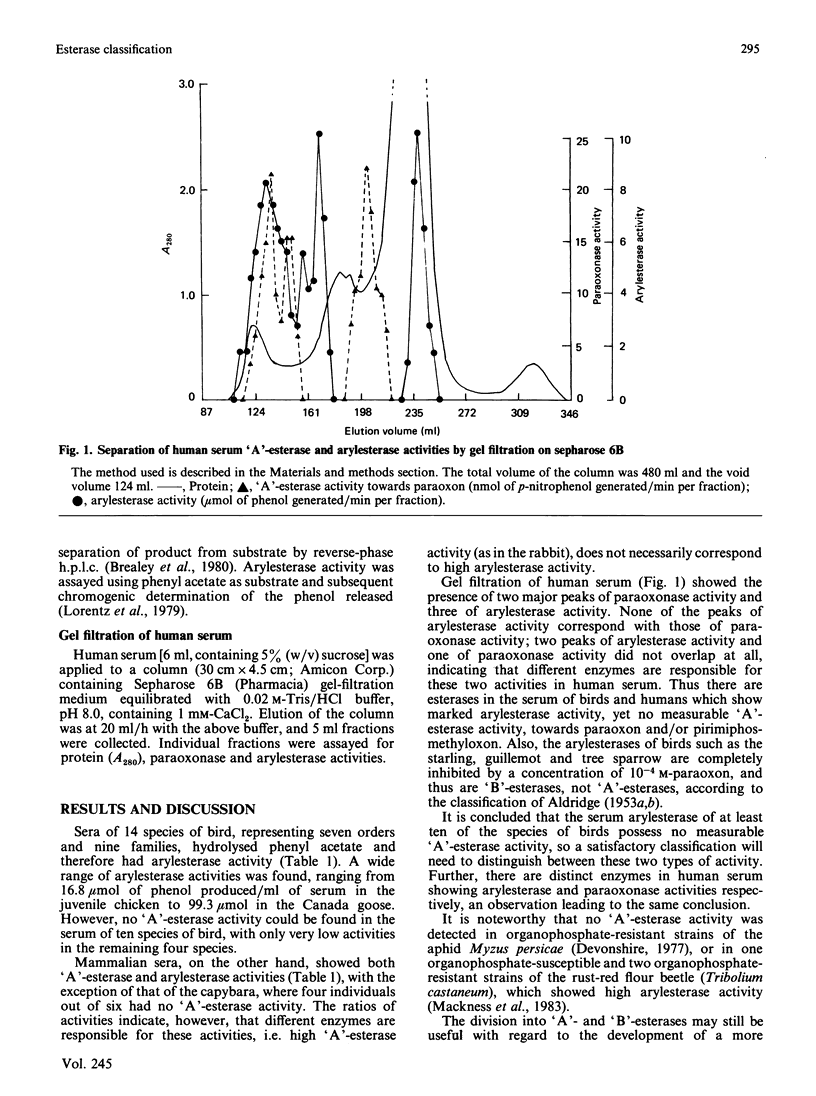
'A'-esterase activities (substrates paraoxon and pirimiphos-methyloxon) and arylesterase activities (substrate phenyl acetate) were assayed in the sera of 14 species of birds representing seven different orders and 11 species of mammal representing five different orders. Ten species of birds had no detectable 'A'-esterase, and the remaining four species only low activity, yet all birds showed considerable arylesterase activity (16.8-99.3 mumol/min per ml of serum). Ten species of mammal showed both 'A'- and 'aryl'-esterase activities. In humans, gel filtration of serum completely separated peaks representing paraoxonase and arylesterase activities. Thus, in both birds and humans, serum enzymes exist that express arylesterase activity but not 'A'-esterase activity. These findings suggest that a distinction should be made between these two types of esterase in future classifications.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALDRIDGE W. N. Serum esterases. I. Two types of esterase (A and B) hydrolysing p-nitrophenyl acetate, propionate and butyrate, and a method for their determination. Biochem J. 1953 Jan;53(1):110–117. doi: 10.1042/bj0530110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALDRIDGE W. N. Serum esterases. II. An enzyme hydrolysing diethyl p-nitrophenyl phosphate (E600) and its identity with the A-esterase of mammalian sera. Biochem J. 1953 Jan;53(1):117–124. doi: 10.1042/bj0530117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carro-Ciampi G., Kadar D., Kalow W. Distribution of serum paraoxon hydrolyzing activities in a Canadian population. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1981 Aug;59(8):904–907. doi: 10.1139/y81-138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devonshire A. L. The properties of a carboxylesterase from the peach-potato aphid, Myzus persicae (Sulz.), and its role in conferring insecticide resistance. Biochem J. 1977 Dec 1;167(3):675–683. doi: 10.1042/bj1670675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckerson H. W., Romson J., Wyte C., La Du B. N. The human serum paraoxonase polymorphism: identification of phenotypes by their response to salts. Am J Hum Genet. 1983 Mar;35(2):214–227. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiberg H., Mohr J., Schmiegelow K., Nielsen L. S., Williamson R. Linkage relationships of paraoxonase (PON) with other markers: indication of PON-cystic fibrosis synteny. Clin Genet. 1985 Oct;28(4):265–271. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1985.tb00400.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Junge W., Krisch K. Current problems on the structure and classification of mammalian liver carboxylesterases (EC 3.1.1.1). Mol Cell Biochem. 1973 May 11;1(1):41–52. doi: 10.1007/BF01659937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krisch K. Enzymatische Hydrolyse von Diäthyl-p-nitrophenylphosphat (E 600) durch menschlichen Serum. Z Klin Chem Klin Biochem. 1968 Jan;6(1):41–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Du B. N., Eckerson H. W. The polymorphic paraoxonase/arylesterase isozymes of human serum. Fed Proc. 1984 May 15;43(8):2338–2341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorentz K., Flatter B., Augustin E. Arylesterase in serum: elaboration and clinical application of a fixed-incubation method. Clin Chem. 1979 Oct;25(10):1714–1720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackness M. I., Walker C. H. Partial purification and properties of sheep serum "A'-esterases. Biochem Pharmacol. 1983 Aug 1;32(15):2291–2296. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(83)90175-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McElveen J., Mackness M. I., Colley C. M., Peard T., Warner S., Walker C. H. Distribution of paraoxon hydrolytic activity in the serum of patients after myocardial infarction. Clin Chem. 1986 Apr;32(4):671–673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pen J., Beintema J. J. Nomenclature of esterases. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 15;240(3):933–933. doi: 10.1042/bj2400933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmiegelow K., Eiberg H., Tsui L. C., Buchwald M., Phelan P. D., Williamson R., Warwick W., Niebuhr E., Mohr J., Schwartz M. Linkage between the loci for cystic fibrosis and paraoxonase. Clin Genet. 1986 May;29(5):374–377. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1986.tb00507.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson N. E. Serum arylesterase levels of activity in twins and their parents. Am J Hum Genet. 1971 Jul;23(4):375–382. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker C. H., Mackness M. I. Esterases: problems of identification and classification. Biochem Pharmacol. 1983 Nov 15;32(22):3265–3269. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(83)90349-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


