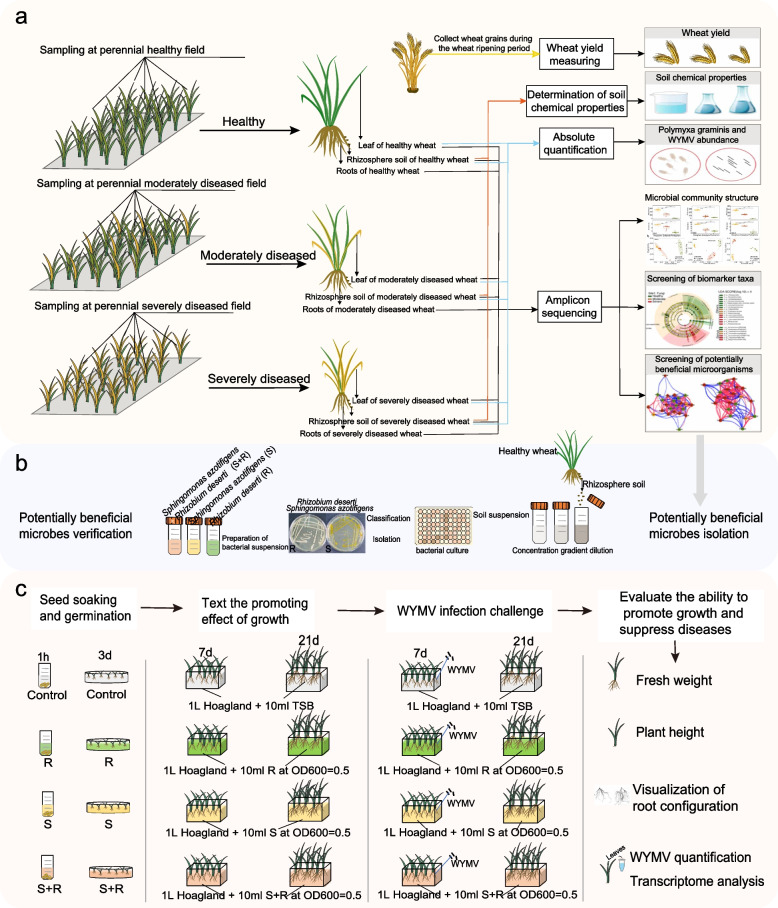
Fig. 1.
The workflow for this study. a The workflow for the field sampling. Sampling was conducted at three sites during the winter wheat seedling stage. At each site, we randomly collected samples from five plants from five healthy plots, five moderately diseased plots, and five severely diseased plots. For each plant, we collected its rhizosphere soil, roots, and leaves. These samples were used for microbial community analysis through 16S rRNA, ITS, and 18S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing. Furthermore, the rhizosphere soil samples were used for the determination of soil chemical properties and quantitative analysis of Polymyxa graminis. RNA was extracted from the leaves for quantitative analysis of wheat yellow mosaic virus (WYMV). At the ripening stage, we harvested all wheat plants and weighed the grain yield at the three sites. b Cultivation and identification of wheat rhizosphere bacteria and the isolation of Sphingomonas azotifigens and Rhizobium deserti. c The workflow of the hydroponic experiment. A WYMV-susceptible wheat cultivar (cv. “LM 4”) was used for the hydroponic experiment. Before treatment, 24 wheat seedlings with similar growth were selected and transplanted into hydroponic boxes containing 1.0 L of sterilized 1/2 Hoagland nutrient solution. Four treatments were included in the experiment: control (sterile TSB solution), inoculation with S. azotifigens only (S), with of R. deserti only (R), and mixed inoculation with S. azotifigens and R. deserti (S + R). Ten milliliters of sterile TSB solution, R, S, and S + R bacterial suspensions (OD600 = 0.5) were inoculated into the sterilized 1/2 Hoagland nutrient solution every day for each treatment. After 7 days of cultivation, 12 plants from each treatment were infected with an equal amount of WYMV via root infection to serve as the infected group, and the remaining 12 wheat plants served as the uninfected control group. Plant samples were collected 14 days after WYMV infection. The height, fresh shoot and root weight, and root architecture of wheat seedlings were measured. The RNA of leaf samples was extracted for WYMV quantification and transcriptome analysis