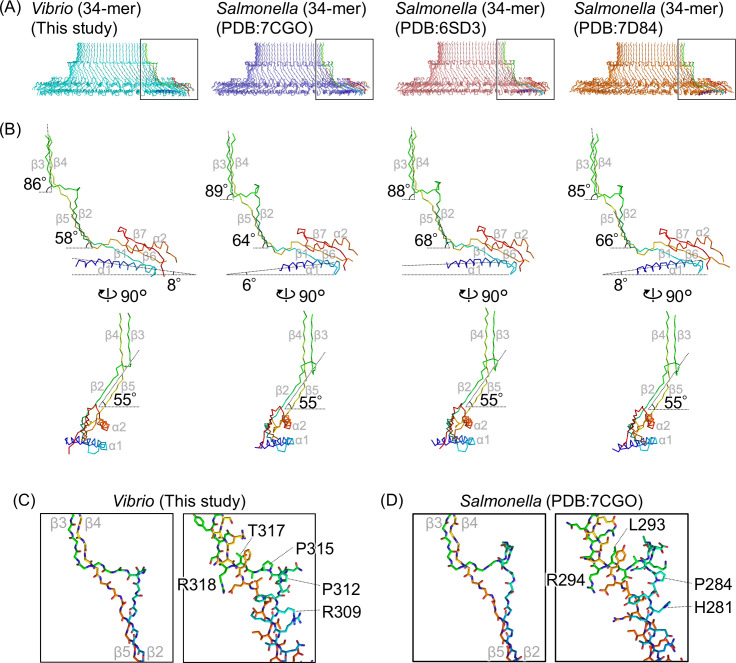
Fig 3.
Comparison of the various S-ring and FliF structures. (A) Cross-section view of the Cα ribbon drawing of the S-ring structures from the MS-ring formed by Vibrio FliFG fusion protein (34-mer, this study), the intact flagellar hook basal body in Salmonella (PDB ID: 7CGO), the MS-ring formed by Salmonella FliF (PDB ID: 6SD3), and the MS-ring formed by Salmonella FliF (PDB ID: 7D84). All have 34-fold rotational symmetry. A protomer in each ring is colored in rainbow. (B) Comparison of FliF protomer structures in the S-rings. The protomers colored in rainbow in panel A are shown. The inclination angles of the RBM3, the antiparallel β2/β5 strands, or the β3/β4 strands relative to the horizontal are shown. (C and D) Comparison of the protruding triangular β2–β3 loops in Vibrio FliF (this study) and Salmonella FliF (PDB ID: 7D84) structures. Left: stick models of the main chains. Right: stick models with the side chains. The secondary structure elements are labeled with gray text in panels B–D.