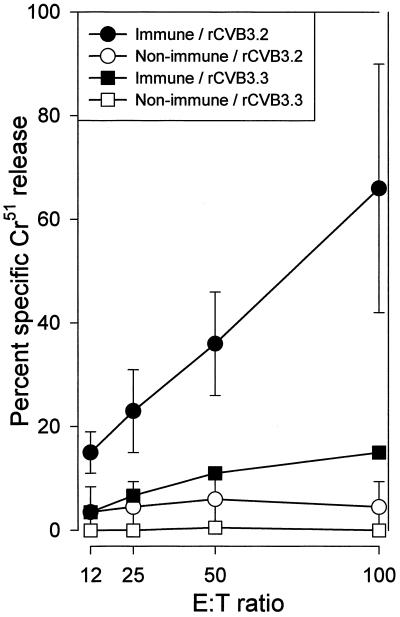
FIG. 6.
rCVB3.2 expresses an LCMV T-cell epitope in vivo. To determine if the artificial LCMV-specific Db-restricted CTL epitope encoded by rCVB3.2 was expressed in vivo, we challenged naive and LCMV-immune C57BL/6 mice with rCVB3.2 and compared the ex vivo epitope-specific CTL response to that in C57BL/6 mice infected with rCVB3.3 expressing an Ld-restricted CTL epitope. At 7 days postinfection, naive mice that were challenged with rCVB3.2 did not exhibit direct ex vivo CTL activity but rCVB3.2 infection of LCMV-immune mice resulted in readily detectable peptide-specific cytotoxicity. This result was not due to bystander activation, since infection of LCMV-immune mice with rCVB3.3 (in this case, encoding an irrelevant T-cell epitope) did not elicit peptide-specific cytolytic activity. The data show the average and standard deviation for two mice per group. Spontaneous lysis of target cells was <20%. E:T ratio, effector-to-target-cell ratio.