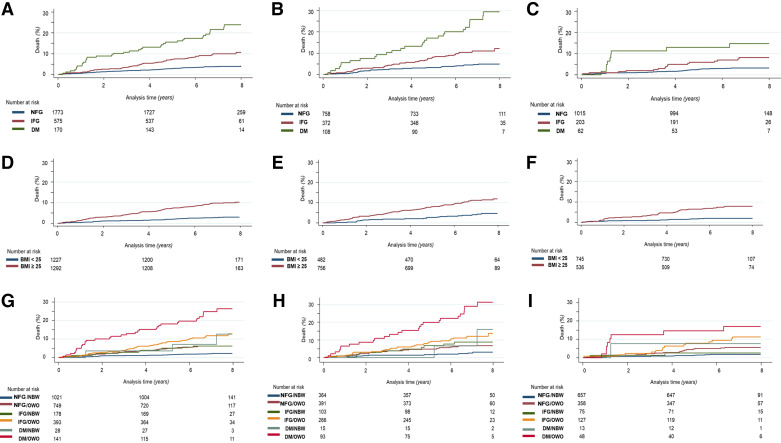
Figure 2.
Incidence of cardiovascular (CV) events and death from CV causes in the follow-up period of CA.ME.LI.A population according to—A: glucose tolerance in the whole population: NFG = 3.84%, IFG = 9.74%, DM = 21.51%; B: glucose tolerance in the male population: NFG = 4.81%, IFG = 10.88%, DM = 25.45%; C: glucose tolerance in the female population: NFG = 3.12%, IFG = 7.69%, DM = 14.55%; D: BMI in the whole population: BMI of <25 (NBW) = 2.96%, BMI of >25 (OWO) = 9.66%; E: BMI in the male population: BMI of <25 (NBW) = 4.47%, BMI of >25 (OWO) = 10.98%; F: BMI in the female population: BMI of <25 (NBW) = 2.15%, BMI of >25 (OWO) = 7.8%; G: BMI and glucose tolerance in the whole population: NFG/NBW = 2.6%, NFG/OWO = 7.0%, DM/NBW = 10.70%, IFG/NBW = 7.5, IFG/OWO = 14.8%, DM/OWO = 24.0%; H: BMI and glucose tolerance in the male population: NFG/NBW = 1.37%, NFG/OWO = 3.76%, DM/NBW = 14.12%, IFG/NBW = 6.37%, IFG/OWO = 9.39%, DM/OWO = 30.28%; I: BMI and glucose tolerance in the female population: NFG/NBW = 1.80%, NFG/OWO = 5.57%, DM/NBW = 7.69%, IFG/NBW = 2.56, IFG/OWO = 10.85%, DM/OWO = 16.67%. BMI, body mass index; CA.ME.LI.A, CArdiovascular risks, MEtabolic syndrome, LIver and Autoimmune disease; DM, diabetes mellitus; IFG, impaired fasting glucose; NBW, normal body weight; NFG, normal fasting glucose; OWO, overweight-obese.