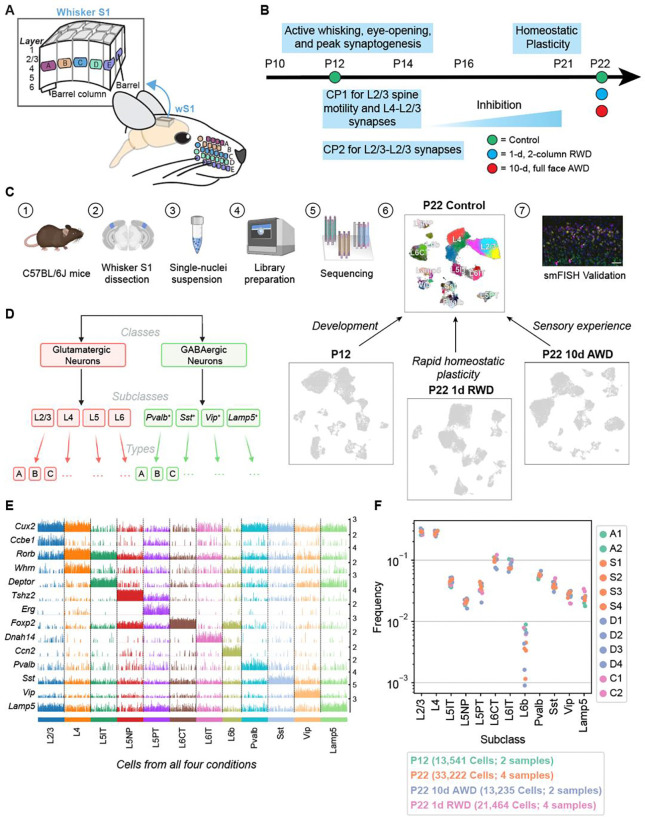
Figure 1. snRNA-seq atlas of the juvenile mouse primary whisker somatosensory cortex (wS1).
(A) Schematic of the mouse whisker somatosensory system, including the facial whisker pad and the whisker somatosensory cortex (wS1). wS1 contains a somatotopic map of the whisker pad in which individual whiskers are represented by neural activity within barrel columns of the cortex. (B) Experimental design and developmental timeline for snRNA-seq profiling of one reference (control) dataset at P22 and three experimental conditions: an earlier time during development (P12) and following two different whisker deprivation paradigms at P22. RWD, row-whisker deprivation. AWD, all-whisker deprivation. (C) General experimental and computational workflow for snRNA-seq profiling and subsequent confirmatory studies. (D) Representation of cortical neuron diversity explored in this study highlighting the three taxonomic levels: classes, subclasses, and types. (E) Tracksplot showing marker genes (rows) for each neuronal subclass (columns). Data was aggregated from 81,456 nuclei across all four conditions and each subclass was subsampled to the size of the smallest subclass for plotting purposes. (F) Relative frequencies of neuronal subclasses are highly consistent across biological replicates and experimental conditions. The highest variance is seen for L6b glutamatergic neurons, whose frequency ranges from 0.1% to 1% of all neurons.