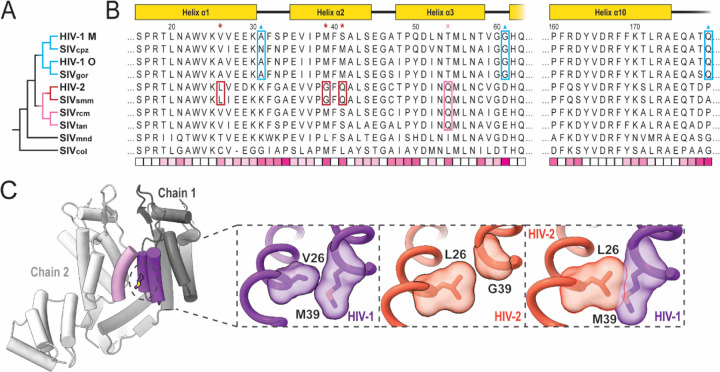
Figure 5:
Mutations implicated in pentamer/hexamer formation among primate lentiviruses.
A. Phylogenetic tree of selected primate lentiviruses based on CA amino acid sequence similarity. B. Multiple sequence alignment of primate lentivirus CA amino acid sequences. Sequences are either from a prior defined group consensus66 or consensus derived from sequences deposited at the Los Alamos National Laboratory database.67 Schematic of HIV-1/HIV-2 domain architecture at the top. Residues marked by red asterisks and boxes are specific to the HIV-2/SIVsmm group. Residue marked by pink cross and box are specific to a broader group of HIV-2-related lentiviruses. Residues marked by blue triangles and boxes are specific changes among the HIV-1-related group. The bottom row displays relative conservation per position based on BLOSUM-80 scoring.68 Highly conserved positions appear whiter while more divergent positions appear more pink. C. Example of the change at position 39 in HIV-134 and HIV-2. Left and central insets highlight the native context of positions 26 and 39 in HIV-1 and HIV-2 with surface representations. Right inset shows aligned HIV-1 and HIV-2 structures with clash between L26 and M39 if without additional changes.