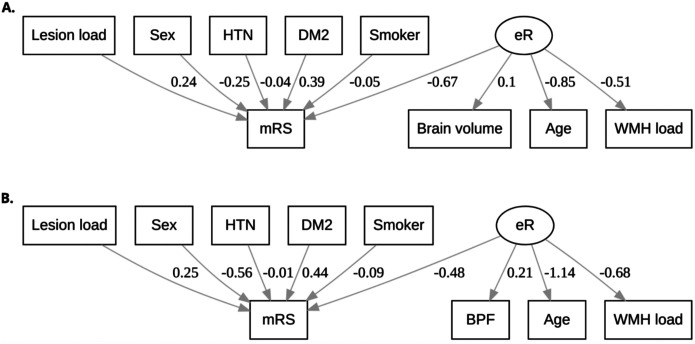
Figure A1.
Al. Structural equation models with estimated associations using path analysis. Model parameters of the brain volume model (Figure A1A) suggest that age and white matter hyperintensity (WMH) load negatively affect effective reserve (eR; path coefficients −0.85 and −0.51, respectively; p<0.001), whereas higher brain volume leads to an increase in eR (path coefficient 0.1; p<0.001). The brain parenchymal fraction (BPF) model (Figure A1B) shows the same trends, with age and WMH load reducing eR (path coefficients −1.14 and −0.68, respectively; p<0.001), and higher BPF, i.e., less brain atrophy, leading to a higher effective reserve. All path coefficients had a p-value of p<0.001 with the brain volume model (A; BIC=4462) outperforming the BPF model (B; BIC=4824). HTN: hypertension; DM2: Diabetes Mellitus Type 2;