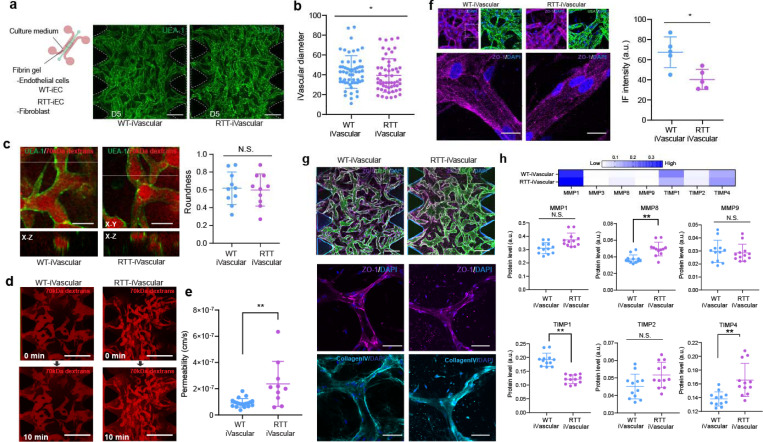
Figure 4. Rett syndrome patient-derived microvascular network exhibited higher permeability along with altered tight junction expression.
(a) WT-iEC and RTT-iEC were embedded in fibrin gel with fibroblast and introduced into microfluidic device to form microvascular networks. Regardless of MeCP2 mutation, microvascular networks were formed with in 5 days. (b) RTT-iVascular exhibited slightly but significantly smaller diameter of vasculature. (c) There is no significant difference of roundness of vasculature. (d) Permeability of endothelial layer were quantified by perfusion of 70 kDa of Texas-red conjugated dextran solution. (e) RTT-iVascular exhibited higher permeability indicating lower barrier function of endothelial layer. (f) Immunostaining of ZO-1 in 3D microvascular networks. ZO-1 intensity in RTT-iVascualr was lower than WT-iVascular. (g) Both WT-iVascular and RTT-iVascular produced collagenIV, but no significant difference. (h) MMP and TIMP1 levels were quantified from condition medium in 3D microvasculature. RTT-iVacular secreted higher MMP8 and TIMP4 and lower TIMP1, but no significant difference in MMP1 and MMP9. .Student’s t-test, **, p<0.01, * p<0.05.