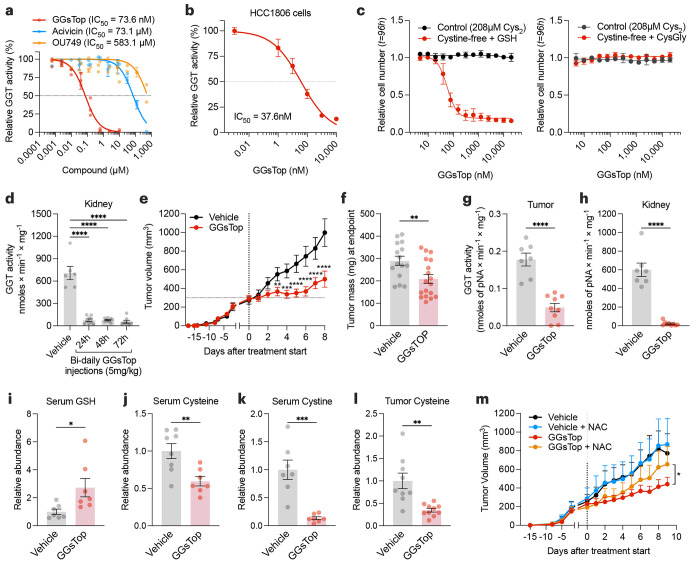
Figure 5. GSH catabolism is necessary to support cysteine supply and tumor growth.
a, Mouse kidney extracts were assayed for GGT activity in the presence of GGT inhibitors. b, HCC-1806 cells were grown in a control medium with indicated doses of GGsTop for 4 hours, and GGT activity was determined. c, Relative cell number of HCC-1806 cells treated with GGsTop for 96 hours in control (208 μM cystine) or cystine-free/GSH- (left) or CysGly-supplemented (right). d, GGT activity in the kidney extracts of C57BL/6 mice treated intraperitoneally with vehicle (n=6 mice) or with 5 mg/kg of GGsTop every 12 hours for 1 (n=9), 2 (n=9), or 3 days (n=8). Statistical significance was evaluated by one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. e, Volume of orthotopically implanted HCC-1806 cell xenografts in mice treated intraperitoneally with vehicle (sterile saline) (n=15) or 5 mg/kg GGsTop (n=18) every 12 hours for 8 days. Statistical significance was assessed by two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. f-h, Tumor mass (f), and GGT activity in tumor (g) and kidney (h) of mice from (e) at the endpoint. i-k, Serum levels of GSH (NEM-GSH) (i), cysteine (NEM-cysteine) (j) and cystine (k) measured by LCMS. l. Tumor levels of cysteine (NEM-cysteine) measured by LCMS. Statistical significance in (f-l) was assessed by unpaired two-tailed t test. m, Volume of orthotopically implanted HCC-1806 cell xenografts in mice treated 5 mg/kg GGsTop every 12 hours while being supplemented with n-acetyl-cysteine (NAC, 30 mM) in their drinking water (Vehicle, n=5 mice; GGsTop, n=8; Vehicle with NAC, n=7, GGsTop with NAC, n=7). Statistical significance was assessed by two-way ANOVA. Data represented as mean ± s.e.m., *p-value<0.05; **p-value<0.01; ***p-value<0.001; ****p-value<0.0001; ns, not significant.