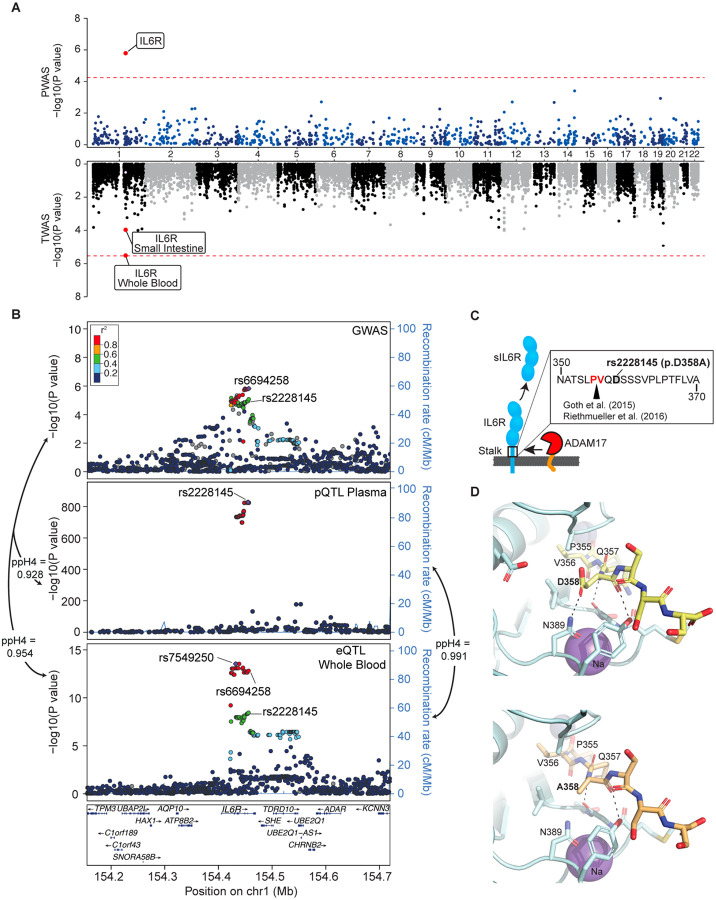
Figure 2. Effects of the IL6R locus.
(A) Miami plot for PWAS and TWAS analyses. The red lines indicate the Bonferroni adjusted significance thresholds (5.6×10−5 for PWAS and 2.5×10−6 for TWAS). (B) Regional association plots for the IL6R locus. SNPs are plotted by position (hg19, 250kb window) versus −log10(P-values) from GWAS of IgAV (top), pQTL of plasma sIL6R levels (middle) and eQTL of IL6R expression in whole blood (bottom). The purple diamond highlights the most significant SNP for each association. SNPs are color-coded to reflect their LD with this SNP using LocusZoom with HapMap CEU reference. The missense variant IL6R p.Asp358Ala (rs2228145) is indicated in each plot. (C) The p.Asp358Ala substitution in relation to the cleavage site of the membrane bound IL6R. (D) Structure of the ADAM17 catalytic domain/IL-6R complex. The structure of ADAM17 (pale cyan ribbon render) was modeled with bound peptide 355-PVQDSSS-361 (yellow sticks in upper panel) or 355-PVQASSS-361 (pale orange sticks in lower panel) corresponding to a segment of the stalk region of IL-6R including the cleavage site (P355/V356). Residues of ADAM17 within 5 angstroms of D358 or A358 are shown as sticks. Polar interactions between residue 358 and ADAM17 are noted by dashed lines. The change D358A eliminates the interaction with N389 of ADAM17, potentially reducing the affinity of IL-6R for ADAM 17. Zinc and Sodium ions are shown as slate and purple spheres, respectively. Images generated with PyMOL (Molecular Graphics System, Version 2.0, Schrödinger, LCC).