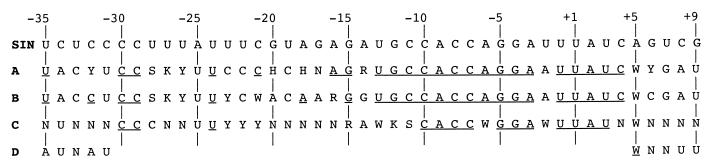
FIG. 4.
SIN promoter. (A) Consensus sequence of the virus populations after three passages on C7-10 cells at 30°C (Fig. 3A). Consensus bases are those that show obvious enrichment over the other bases (Fig. 3A). Bases that were found to be wild type are underlined. Positions that appeared to prefer more than one base are designated by the standard single-letter code (R = G or A; Y = U or C; S = G or C; W = A or U; K = G or U; H = A, U, or C; D = A, G, or U; N = A, C, G, or U). (B) Consensus sequence of individual clones sampled from the C7-10 P3 virus population (Table 3). Unambiguous bases are those found at a frequency of ≥0.6, except for positions −25 and −16, where the dominant base had a frequency of 0.5 but the other bases each had frequency of ≤0.2. (C). Consensus sequence of the virus populations after four passages on BHK-21 cells at 37°C (Fig. 3B). (D) Consensus sequence of the −35 and +5 virus populations after four passages on BHK-21 cells at 30°C (Fig. 3B). Blanks indicate that populations were not tested.