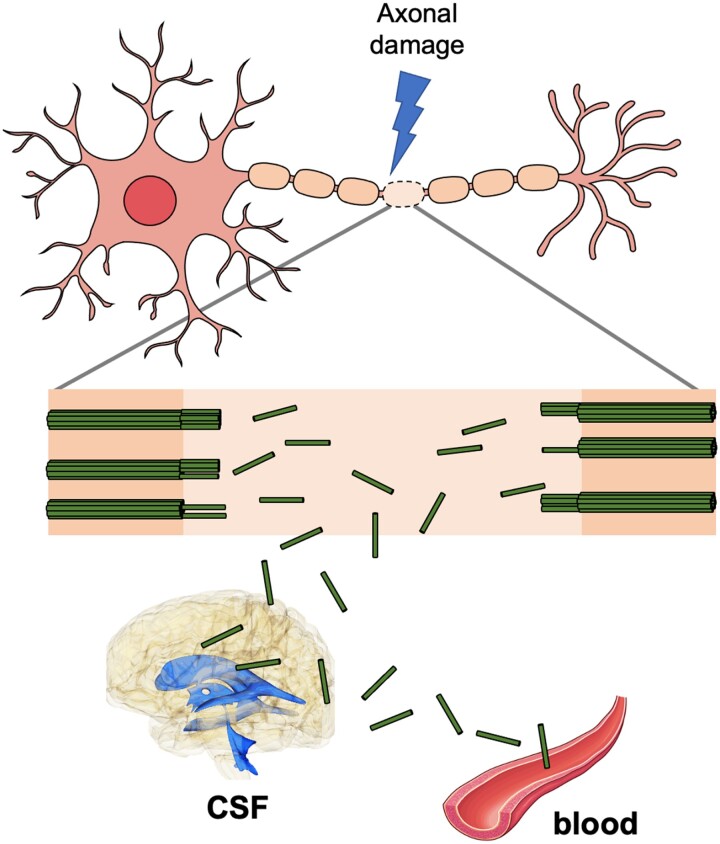
Figure 1.
Influx of NfL into the CSF and the bloodstream following axonal damage. Following damage to axons, the fragments of neurofilament chains (green sticks) are released into the CSF and the bloodstream. The mechanisms of the influx of neurofilament light chain (NfL) into CSF and blood are not yet clearly known. See Gafson et al.3 and Yuan and Nixon4 for discussions on potential CSF drainage pathways responsible for the entry of NfL into CSF. A possible route for the influx of NfL fragments into the blood is the drainage of NfL-containing CSF to dural venous sinuses through arachnoid villi.5 The figure contains images adapted from an icon, ‘Motor neuron’ (https://reactome.org/content/detail/R-ICO-014093) by reactome.org, used under CC BY 4.0, and an image, ‘Arteries’ (https://smart.servier.com/smart_image/artery-20/) by Servier Medical Art, used under CC BY 3.0.