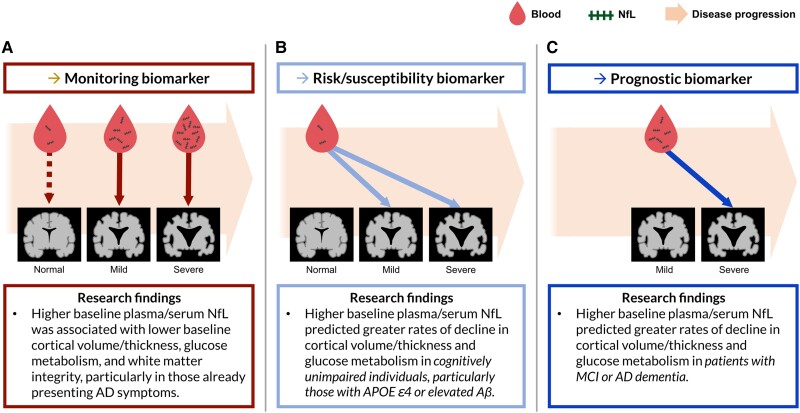
Figure 3.
The potential roles of blood-based NfL as different types of biomarkers and supporting research findings. (A) Plasma/serum neurofilament light chain (NfL) has been correlated with neurodegeneration at the time of the blood draw in patients showing cognitive impairment. This supports the potential utility of plasma/serum NfL as a monitoring biomarker indicating the severity of neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's disease (AD). The dashed red line represents weak correlations between NfL and neurodegeneration in those without cognitive decline. (B) Plasma/serum NfL in cognitively unimpaired individuals has predicted the subsequent rate of neurodegeneration in brain areas susceptible to AD, supporting the potential utility of plasma/serum NfL as a risk/susceptibility biomarker for AD. (C) Plasma/serum NfL in individuals showing the symptoms of AD has predicted the subsequent rate of neurodegeneration, suggesting that plasma/serum NfL is a promising prognostic biomarker for neurodegeneration in patients with AD. Aβ = amyloid-β; MCI = mild cognitive impairment. The figure contains images adapted from ‘Alzheimer disease’ (https://smart.servier.com/smart_image/alzheimer-3/) by Servier Medical Art, used under CC BY 3.0.