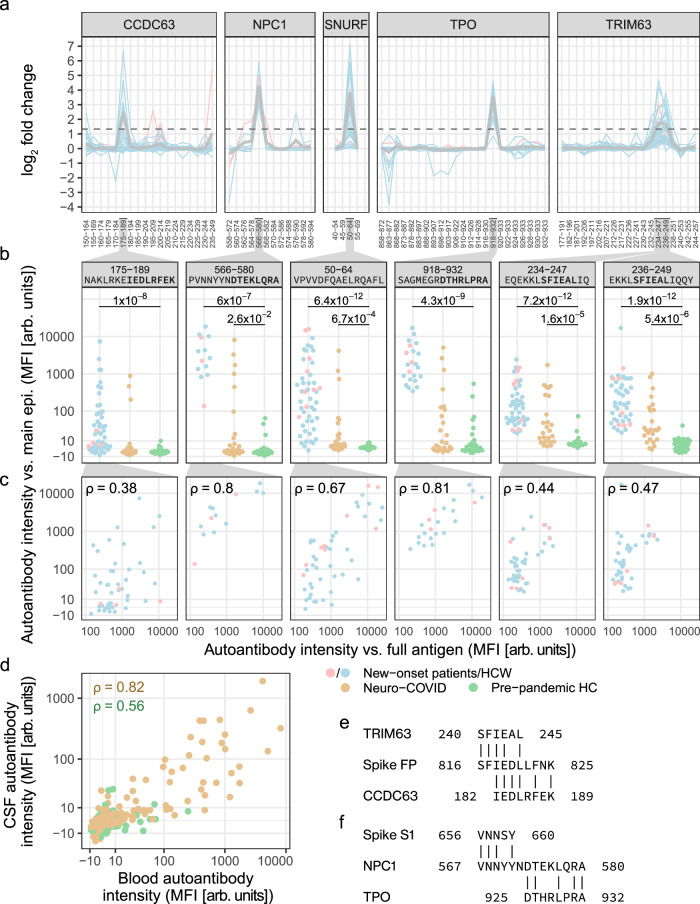
Fig. 5. The main epitopes of new-onset autoantibodies are elevated in blood and CSF of an independent cohort with neuro-COVID and align with the SARS-CoV-2 fusion peptide.
a Epitope mapping revealed the main epitopes of six new-onset autoantibodies. Lines depict epitope profiles (anti-peptide IgG log2 fold change (FC)) at new-onset in individuals with the corresponding new-onset autoantibody. Gray lines depict the mean. The dashed line indicates the cutoff for classification as a main epitope (FC ≥2.52). Numbering on the x-axis corresponds to the peptide amino acid positions in the full-length protein (Supplementary Data 3). b Antibodies against the main epitopes were elevated in an independent cohort of neuro-COVID patients compared to pre-pandemic HCs. Brackets indicate a statistically significant difference to pre-pandemic HC (q values ≤ 0.05 from two-sided Mann–Whitney U tests with Benjamini–Hochberg correction). The y-axis displays signal intensity on the pseudo-log10 scale. c Correlation of autoantibody intensity against the main epitopes (epi., y-axis) and the full antigen (x-axis). ρ Spearman’s rho. d Correlation of autoantibodies against the main epitopes in blood and CSF of neuro-COVID patients and pre-pandemic HCs. Data points correspond to paired blood and CSF samples in neuro-COVID patients (n = 23) and HCs (n = 21), and the peptides shown in panel (b). e, f Sequence similarity between (e) the main epitopes of TRIM63 and CCDC63 to the SARS-CoV-2 Spike fusion peptide, and f between the main epitopes of TPO and NPC1 and the C-terminal domain of Spike S1. MFI median fluorescent intensity, HC healthy controls, HCW healthcare workers. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.