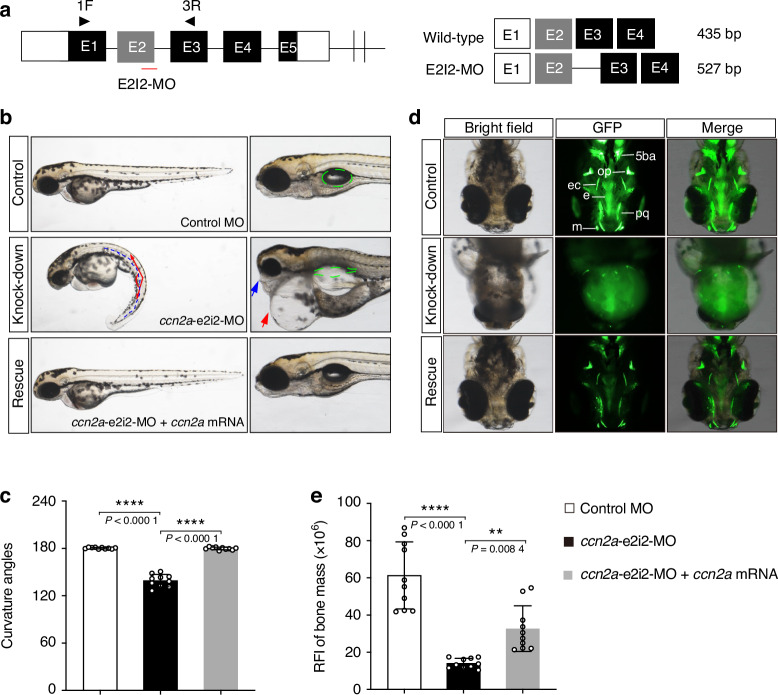
Fig. 5.
Overexpression of ccn2a mRNA rescues morphological abnormalities and craniofacial phenotypes in ccn2a knockdown zebrafish. a Zebrafish ccn2a gene is targeted by specific morpholino antisense to prevent proper splicing of exon 2 (E2I2-MO). Primers 1 F and 3 R interrogate the presence of wild type transcripts or those in which intron 2 has been inserted. The diagram is a schematic depiction of the intron 2 inserted transcript in the E2I2-MO injected embryos (527 bp) as compared with control MO injected embryos (435 bp). b Representative lateral views of zebrafish at 2 days post-fertilization (dpf) injected with either control MO or ccn2a MO with or without ccn2a mRNA. The ccn2a morphants display curved body axis (blue dotted line), small eyes, pericardial oedema (red arrow), jaw defects (blue arrow), and non-inflated swim bladder (green circled area). Co-injection of nonmutant zebrafish ccn2a mRNA rescue the gross morphology in ccn2a morphants. c Quantification of the average curvature angle of zebrafish in each group at 2-dpf. Data are represented as mean ± SD (n = 10). One way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post hoc multiple comparisons was used. ****P < 0.000 1. d Representative ventral view of the craniofacial skeleton of zebrafish in each group at 5-dpf labeled with calcein. 5ba, fifth branchial arch; op, opercular bone; ec, ectopterygoid; e, ethmoid plate; pq, palatoquadrate; m, Meckel’s cartilage. Co-injection of nonmutant zebrafish ccn2a mRNA significantly rescued head skeletal malformation in ccn2a morphants. e Quantification of the relative fluorescence intensity (RFI) of craniofacial skeleton bone mass of zebrafish in each group at 5-dpf (n = 10). Data are represented as mean ± SD. One way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post hoc multiple comparisons was used. **P < 0.01; ****P < 0.000 1