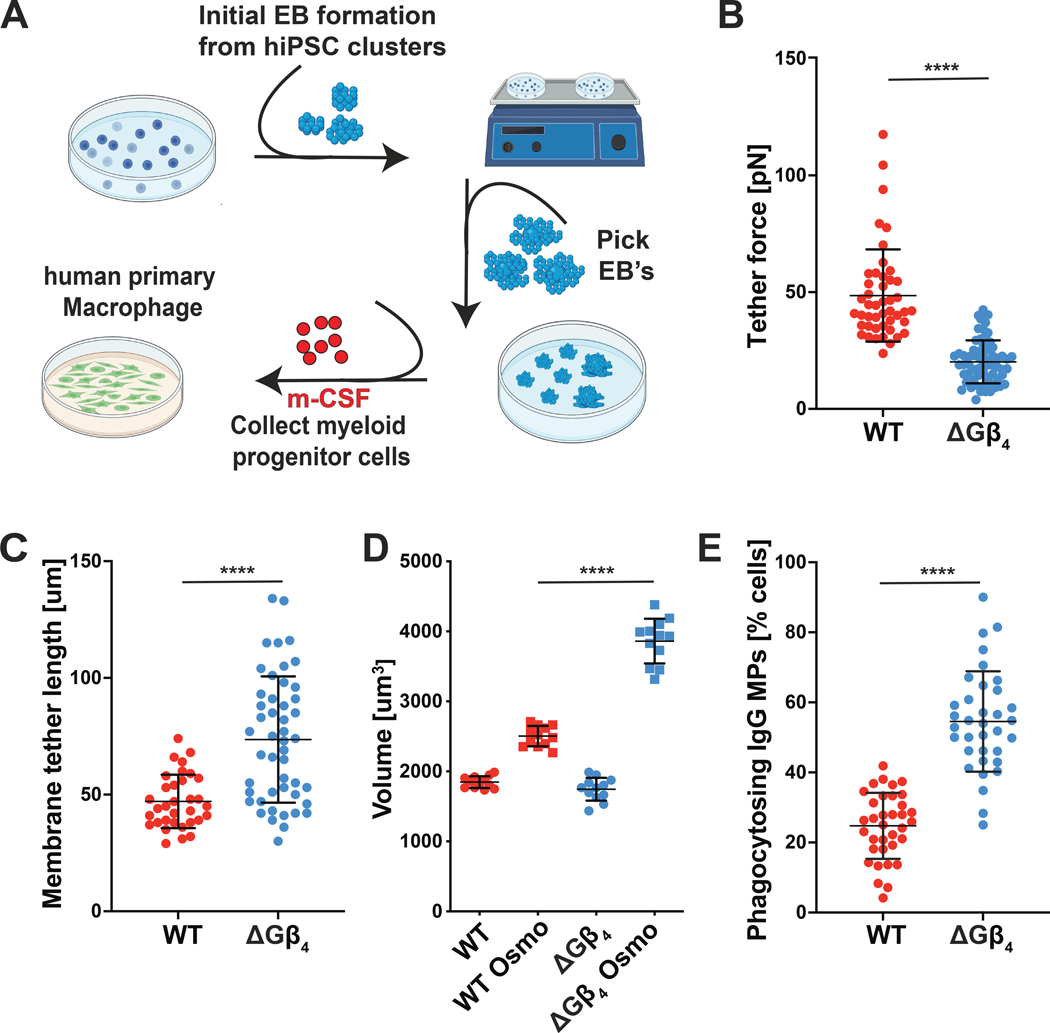
Fig 6: Gβ4 deficiency boosts primary macrophage phagocytosis.
A-D, Isogenic ΔGβ4 and WT macrophages were derived from hiPSCs and subjected to biophysical and functional assays. A, Schematic of embryoid body generation from hiPSCs and differentiation of primary macrophages from GMPs. B-C, Membrane tethers were generated from WT and ΔGβ4 macrophages using an optical trap. B, Quantification of membrane tether force. C, Quantification of membrane tether length. Data in B-C represent mean ± s.d. n ≥ 46 for each sample, pooled from 5 biological replicates. D, ΔGβ4 and WT macrophages were osmotically shocked and allowed to expand to their full volume to assess total plasma membrane. Data represent mean ± s.d. n = 12 for each sample, pooled from 3 biological replicates. E, WT and ΔGβ4 macrophages were challenged with IgG-coated MPs for 2 h and phagocytic uptake quantified by florescence microscopy. Data represent mean ± s.d., pooled from 5 biological replicates. Unpaired t-test (B, C, E) or two-way ANOVA (D), **** p< 0.0001.