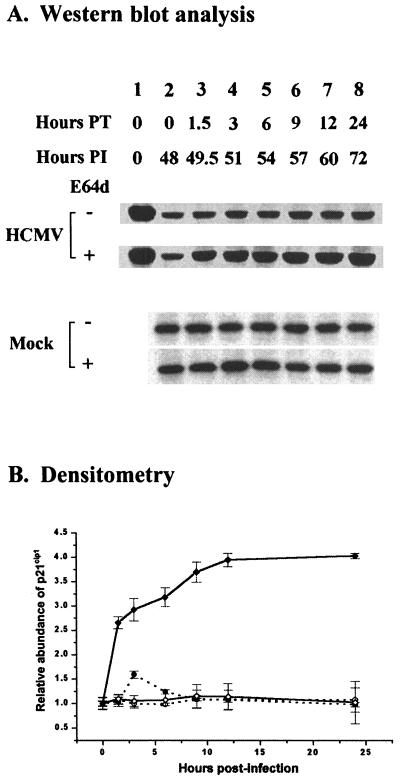
FIG. 3.
Cumulative effect of the calpain inhibitor E64d (100 μM) on p21cip1 protein levels in HCMV- or mock-infected, density-arrested LU cells. (A) LU cells arrested by contact inhibition as described in Materials and Methods were infected with HCMV (5 PFU/cell) or mock infected and then exposed to E64d beginning at 48 h p.i. At the times indicated, whole-cell lysates were prepared, and 40 μg of protein from each lysate was analyzed by SDS-PAGE. The proteins were transferred to nitrocellulose and probed with antibodies against p21cip1. The results of a representative experiment are shown. Hours PT (posttreatment) indicates the duration of E64d exposure. Hours PI indicates the time of harvest after infection. The exposure time for blots of lysates from HCMV-infected cells was about three times longer than that required for blots of lysates from mock-infected cells. Accordingly, to permit a quantitative comparison between the p21cip1 abundance at 0 h p.i. and at later times, lane 1 for the HCMV-infected cell lysates was loaded with a lysate from mock-infected cells not treated with E64d. (B) Accumulation of p21cip1 after E64d treatment, determined by densitometry of the data illustrated in panel A and from two additional experiments. The results for p21cip1 abundance in HCMV- and mock-infected cells with standard deviation shown are plotted relative to the p21cip1 abundance at 0 h in the absence of E64d in HCMV- and mock-infected cells, respectively (○, mock-infected cells; ●, mock-infected cells treated with E64d; ◊, HCMV-infected cells; ⧫, HCMV-infected cells treated with E64d).