Abstract
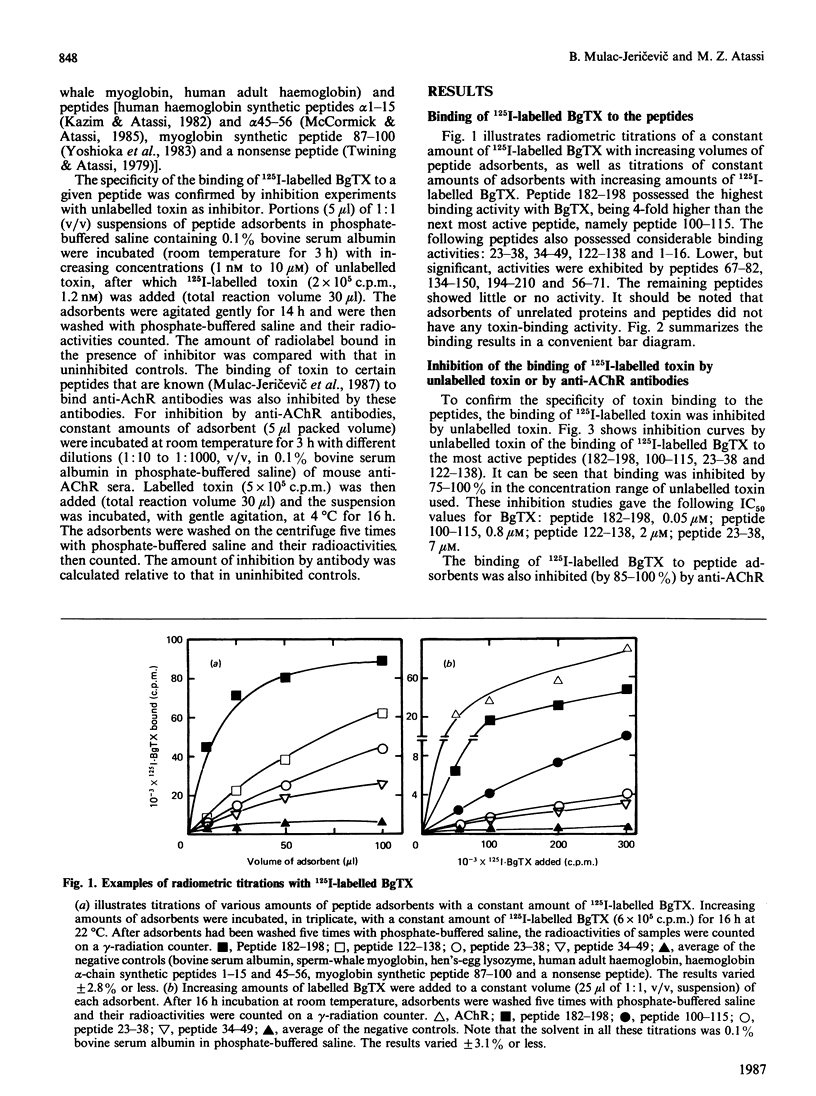
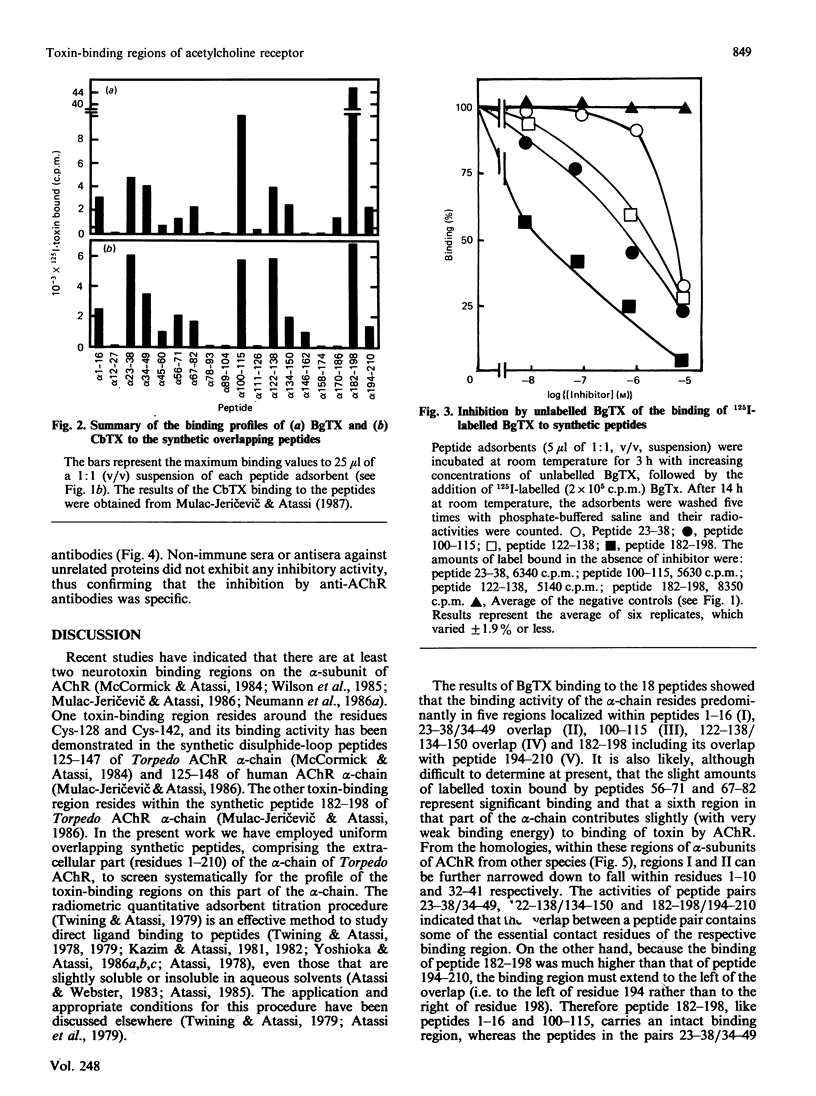
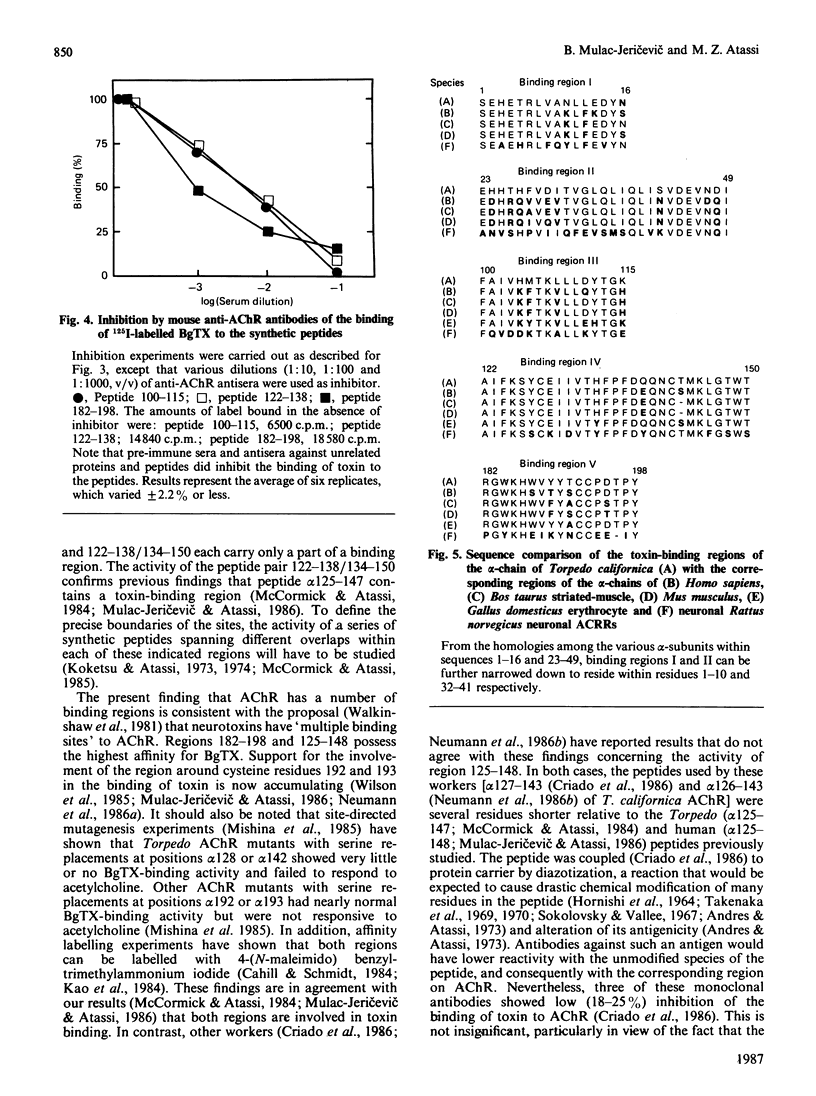
The continuous alpha-neurotoxin-binding regions on the extracellular part (residues 1-210) of the alpha-chain of Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor were localized by reaction of 125I-labelled alpha-bungarotoxin with synthetic overlapping peptides spanning this entire part of the chain. The specificity of the binding was confirmed by inhibition with unlabelled toxin and, for appropriate peptides, with unlabelled anti-(acetylcholine receptor) antibodies. Five toxin-binding regions were localized within residues 1-10, 32-41, 100-115, 122-150 and 182-198. The third, fourth and fifth (and to a lesser extent the first and second) toxin-binding regions overlapped with regions recognized by anti-(acetylcholine receptor) antibodies. The five toxin-binding regions may be distinct sites or, alternatively, different 'faces' in one (or more) sites.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andres S. F., Atassi M. Z. Immunochemistry of sperm-whale myoglobin. Conformation and immunochemistry of derivatives prepared by reaction with diazonium-1H-tetrazole. Evaluation of the specificity of the reagent. Biochemistry. 1973 Feb 27;12(5):942–947. doi: 10.1021/bi00729a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atassi M. Z. Precise determination of the entire antigenic structure of lysozyme: molecular features of protein antigenic structures and potential of "surface-simulation" synthesis--a powerful new concept for protein binding sites. Immunochemistry. 1978 Dec;15(12):909–936. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90126-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atassi M. Z., Sakata S., Kazim A. L. Localization and verification by synthesis of five antigenic sites of bovine serum albumin. Biochem J. 1979 May 1;179(2):327–331. doi: 10.1042/bj1790327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atassi M. Z. Surface-simulation synthesis of the substrate-binding site of an enzyme. Demonstration with trypsin. Biochem J. 1985 Mar 1;226(2):477–485. doi: 10.1042/bj2260477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atassi M. Z., Webster R. G. Localization, synthesis, and activity of an antigenic site on influenza virus hemagglutinin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):840–844. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballivet M., Nef P., Stalder R., Fulpius B. Genomic sequences encoding the alpha-subunit of acetylcholine receptor are conserved in evolution. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;48(Pt 1):83–87. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.048.01.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulter J., Evans K., Goldman D., Martin G., Treco D., Heinemann S., Patrick J. Isolation of a cDNA clone coding for a possible neural nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alpha-subunit. 1986 Jan 30-Feb 5Nature. 319(6052):368–374. doi: 10.1038/319368a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulter J., Luyten W., Evans K., Mason P., Ballivet M., Goldman D., Stengelin S., Martin G., Heinemann S., Patrick J. Isolation of a clone coding for the alpha-subunit of a mouse acetylcholine receptor. J Neurosci. 1985 Sep;5(9):2545–2552. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-09-02545.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahill S., Schmidt J. An immunochemical approach to the identification of the MBTA binding site of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor of Torpedo californica. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jul 31;122(2):602–608. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80075-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Changeux J. P., Devillers-Thiéry A., Chemouilli P. Acetylcholine receptor: an allosteric protein. Science. 1984 Sep 21;225(4668):1335–1345. doi: 10.1126/science.6382611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Changeux J. P. The acetylcholine receptor: an "allosteric" membrane protein. Harvey Lect. 1979 1980;75:85–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claudio T., Ballivet M., Patrick J., Heinemann S. Nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences of Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor gamma subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):1111–1115. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.1111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conti-Tronconi B. M., Raftery M. A. The nicotinic cholinergic receptor: correlation of molecular structure with functional properties. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:491–530. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.002423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Criado M., Hochschwender S., Sarin V., Fox J. L., Lindstrom J. Evidence for unpredicted transmembrane domains in acetylcholine receptor subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):2004–2008. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Criado M., Sarin V., Fox J. L., Lindstrom J. Evidence that the acetylcholine binding site is not formed by the sequence alpha 127-143 of the acetylcholine receptor. Biochemistry. 1986 May 20;25(10):2839–2846. doi: 10.1021/bi00358a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finer-Moore J., Stroud R. M. Amphipathic analysis and possible formation of the ion channel in an acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):155–159. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froehner S. C., Rafto S. Comparison of the subunits of Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor by peptide mapping. Biochemistry. 1979 Jan 23;18(2):301–307. doi: 10.1021/bi00569a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy H. R. A structural model of the acetylcholine receptor channel based on partition energy and helix packing calculations. Biophys J. 1984 Jan;45(1):249–261. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84152-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HORINISHI H., HACHIMORI Y., KURIHARA K., SHIBATA K. STATES OF AMINO ACID RESIDUES IN PROTEINS. 3. HISTIDINE RESIDUES IN INSULIN, LYSOZYME, ALBUMIN AND PROTEINASES AS DETERMINED WITH A NEW REAGENT OF DIAZO-I-H-TETRAZOLE. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Jun 8;86:477–489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hucho F. The nicotinic acetylcholine receptor and its ion channel. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Jul 15;158(2):211–226. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09740.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazim A. L., Atassi M. Z. A novel and comprehensive synthetic approach for the elucidation of protein antigenic structures. Determination of the full antigenic profile of the alpha-chain of human haemoglobin. Biochem J. 1980 Oct 1;191(1):261–264. doi: 10.1042/bj1910261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazim A. L., Atassi M. Z. Haemoglobin binding with haptoglobin. Localization of the haptoglobin-binding site on the alpha-chain of human haemoglobin. Biochem J. 1981 Aug 1;197(2):507–510. doi: 10.1042/bj1970507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazim A. L., Atassi M. Z. Structurally inherent antigenic sites. Localization of the antigenic sites of the alpha-chain of human haemoglobin in three host species by a comprehensive synthetic approach. Biochem J. 1982 Apr 1;203(1):201–208. doi: 10.1042/bj2030201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koketsu J., Atassi M. Z. Immunochemistry of sperm-whale myoglobin. 18. Accurate delineation of the single reactive region in sequence 120-153 by study of synthetic peptides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Dec 6;328(2):289–302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koketsu J., Atassi M. Z. Immunochemistry of sperm-whale myoglobin. XVI. Accurate delineation of the single region in sequence 1-55 by immunochemical studies of synthetic peptides. Some conclusions concerning antigenic structures of proteins. Immunochemistry. 1974 Jan;11(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(74)90335-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. L., Atassi M. Z. Enzymic and immunochemical properties of lysozyme. Accurate definition of the antigenic site around the disulphide bridge 30-115 (site 3) by 'surface-simulation' synthesis. Biochem J. 1977 Dec 1;167(3):571–581. doi: 10.1042/bj1670571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennon V. A., McCormick D. J., Lambert E. H., Griesmann G. E., Atassi M. Z. Region of peptide 125-147 of acetylcholine receptor alpha subunit is exposed at neuromuscular junction and induces experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis, T-cell immunity, and modulating autoantibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8805–8809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy M. P., Earnest J. P., Young E. F., Choe S., Stroud R. M. The molecular neurobiology of the acetylcholine receptor. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1986;9:383–413. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.09.030186.002123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick D. J., Atassi M. Z. Localization and synthesis of the acetylcholine-binding site in the alpha-chain of the Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor. Biochem J. 1984 Dec 15;224(3):995–1000. doi: 10.1042/bj2240995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishina M., Tobimatsu T., Imoto K., Tanaka K., Fujita Y., Fukuda K., Kurasaki M., Takahashi H., Morimoto Y., Hirose T. Location of functional regions of acetylcholine receptor alpha-subunit by site-directed mutagenesis. 1985 Jan 31-Feb 6Nature. 313(6001):364–369. doi: 10.1038/313364a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore H. P., Raftery M. A. Studies of reversible and irreversible interactions of an alkylating agonist with Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor in membrane-bound and purified states. Biochemistry. 1979 May 15;18(10):1862–1867. doi: 10.1021/bi00577a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulac-Jericevic B., Atassi M. Z. Segment alpha 182-198 of Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor contains second toxin-binding region and binds anti-receptor antibodies. FEBS Lett. 1986 Apr 7;199(1):68–74. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81225-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulac-Jericević B., Kurisaki J., Atassi M. Z. Profile of the continuous antigenic regions on the extracellular part of the alpha chain of an acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3633–3637. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann D., Barchan D., Fridkin M., Fuchs S. Analysis of ligand binding to the synthetic dodecapeptide 185-196 of the acetylcholine receptor alpha subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9250–9253. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann D., Barchan D., Safran A., Gershoni J. M., Fuchs S. Mapping of the alpha-bungarotoxin binding site within the alpha subunit of the acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):3008–3011. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.3008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Furutani Y., Takahashi H., Toyosato M., Tanabe T., Shimizu S., Kikyotani S., Kayano T., Hirose T., Inayama S. Cloning and sequence analysis of calf cDNA and human genomic DNA encoding alpha-subunit precursor of muscle acetylcholine receptor. 1983 Oct 27-Nov 2Nature. 305(5937):818–823. doi: 10.1038/305818a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Takahashi H., Tanabe T., Toyosato M., Furutani Y., Hirose T., Asai M., Inayama S., Miyata T., Numa S. Primary structure of alpha-subunit precursor of Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor deduced from cDNA sequence. Nature. 1982 Oct 28;299(5886):793–797. doi: 10.1038/299793a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Takahashi H., Tanabe T., Toyosato M., Kikyotani S., Furutani Y., Hirose T., Takashima H., Inayama S., Miyata T. Structural homology of Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor subunits. Nature. 1983 Apr 7;302(5908):528–532. doi: 10.1038/302528a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patrick J., Stallcup W. B. Immunological distinction between acetylcholine receptor and the alpha-bungarotoxin-binding component on sympathetic neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4689–4692. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobel A., Weber M., Changeux J. P. Large-scale purification of the acetylcholine-receptor protein in its membrane-bound and detergent-extracted forms from Torpedo marmorata electric organ. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Oct 17;80(1):215–224. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11874.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokolovsky M., Vallee B. L. Azocarboxypeptidase: functional consequences of tyrosyl and histidyl modification. Biochemistry. 1967 Mar;6(3):700–708. doi: 10.1021/bi00855a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takenaka A., Suzuki T., Takenaka O., Horinishi H., Shibata K. States of amino acid residues in proteins. 18. A revised way of using diazonium-I-H-tetrazole for reactivity examination of histidine and tyrosine residues. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Nov 11;194(1):293–300. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(69)90206-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takenaka A., Takenaka O., Horinishi H., Shibata K. States of amino acid residues in proteins. XXII. Effect of cyanide on the reactivities of histidine and tyrosine residues in ferrihemoglobin and ferrimyoglobin. J Biochem. 1970 Mar;67(3):397–402. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twining S. S., Atassi M. Z. Antibody-combining sites can be mimicked synthetically. Surface-simulation synthesis of the immunoglobulin new combining site to the gamma-hydroxyl derivative of vitamin K1. J Biol Chem. 1978 Aug 10;253(15):5259–5262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twining S. S., Atassi M. Z. Use of immunoadsorbents for the study of antibody binding to sperm whale myoglobin and its synthetic antigenic sites. J Immunol Methods. 1979;30(2):139–151. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90088-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzartos S. J., Changeux J. P. High affinity binding of alpha-bungarotoxin to the purified alpha-subunit and to its 27,000-dalton proteolytic peptide from Torpedo marmorata acetylcholine receptor. Requirement for sodium dodecyl sulfate. EMBO J. 1983;2(3):381–387. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01434.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson P. T., Lentz T. L., Hawrot E. Determination of the primary amino acid sequence specifying the alpha-bungarotoxin binding site on the alpha subunit of the acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8790–8794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshioka M., Bixler G. S., Jr, Atassi M. Z. Preparation of T-lymphocyte lines and clones with specificities to preselected protein sites by in vitro passage with free synthetic peptides: demonstration with myoglobin sites. Mol Immunol. 1983 Oct;20(10):1133–1137. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(83)90123-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshioka N., Atassi M. Z. Antigenic structure of human haemoglobin. Localization of the antigenic sites of the beta-chain in three host species by synthetic overlapping peptides representing the entire chain. Biochem J. 1986 Mar 1;234(2):441–447. doi: 10.1042/bj2340441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshioka N., Atassi M. Z. Haemoglobin binding with haptoglobin. Localization of the haptoglobin-binding sites on the beta-chain of human haemoglobin by synthetic overlapping peptides encompassing the entire chain. Biochem J. 1986 Mar 1;234(2):453–456. doi: 10.1042/bj2340453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshioka N., Atassi M. Z. Subunit interacting surfaces of human haemoglobin. Localization of the alpha-subunit-beta-subunit interacting surfaces on the beta-chain by a comprehensive synthetic strategy. Biochem J. 1986 Mar 1;234(2):457–461. doi: 10.1042/bj2340457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


