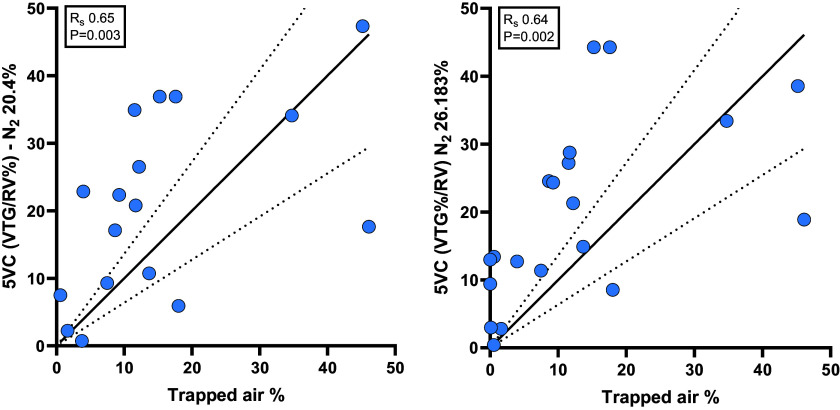
Figure 3.
We used the linear regression slope values from Fig. 2, to update the fundamental assumption of 78% N2 (16) concentration to find a better agreement between the 5-breath methods and trapped air %. For the 5 inspiratory capacity breaths (5IC) method, the 1/slope value was 3.823 whereas for the 5 vital capacity (5VC) method, the 1/slope value was 2.979. Therefore, we recalculated the volume of trapped gas (VTG)/residual volume (RV)% for the 5IC method using a N2 of 20.40% (78/3.823) and 5VC breaths using a N2 of 26.183% (78/2.979) (Fig. 4). As would be expected, the correlation coefficient for both parameters stayed the same, but now the agreement on the extent of trapped air % was almost perfect with a 1/slope 1.00 for both parameters.