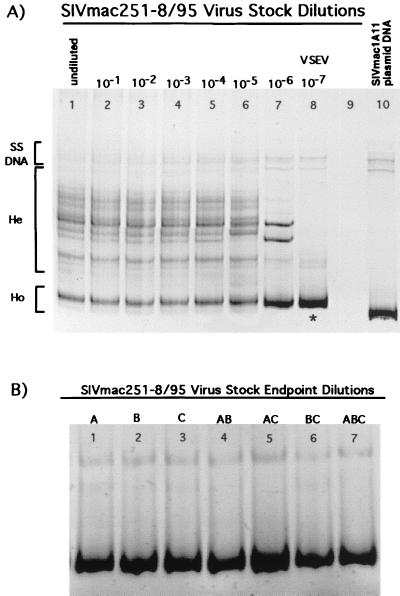
FIG. 1.
SIV V1-V2 variants present in serial dilutions of SIVmac251-8/95 virus stock. (A) Lanes 1 to 8, dilutions of virus stock from undiluted to 10−7. Heteroduplex (He) bands indicate the presence of multiple V1-V2 variants in the virus stock. The last dilution yielding a RT-PCR product (10−7) was comprised of a homogeneous variant population (i.e., a single variant) as depicted by the presence of a single homoduplex (Ho) band in lane 8. The V1-V2 sequence amplified from the 10−7 dilution (∗) was considered to be the most common envelope variant in the virus stock; this variant was designated VSEV. Lane 9, no sample loaded. Lane 10 contains the V1-V2 fragment of SIV amplified from SIVmac1A11 plasmid DNA. This clonal variant population is represented by a single homoduplex band on the gel and is included for comparison of the virus stock V1-V2 variants with a known reference variant. (B) SIV V1-V2 variants present in three separate endpoint dilutions (A to C) of SIVmac251-8/95 virus stock. Mixtures of the RT-PCR products from each of these three endpoint dilutions show they share the same DNA sequence in the V1-V2 envelope region and thus represent the same SIV variant. Lanes: 1, variant amplified from the endpoint of dilution A; 2, variant amplified from the endpoint of dilution B; 3, variant amplified from the endpoint of dilution C; 4, endpoint dilution variant A mixed with endpoint dilution variant B; 5, endpoint dilution variant A mixed with endpoint dilution variant C; 6, endpoint dilution variant B mixed with endpoint dilution variant C; 7, endpoint dilution variant A mixed with endpoint dilution variant B and endpoint dilution variant C.