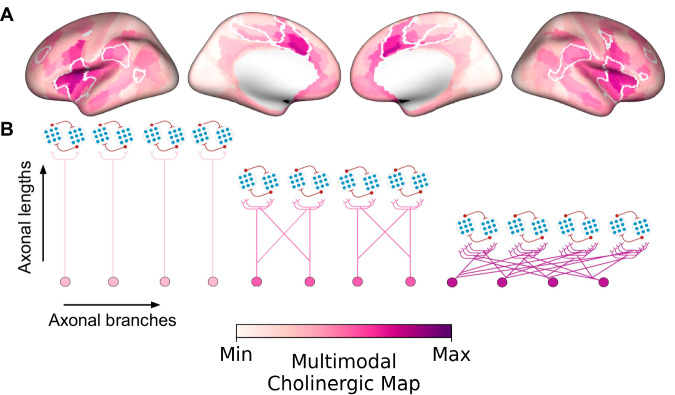
Fig. 8. Multimodal map of the human basal forebrain (BF) cholinergic innervation.
A A cortical surface emphasizing the arborization gradient of BF cholinergic neurons was constructed by summing the intensity normalized maps encoding (1) BF structure-function tethering, (2) cortical VAChT concentration, and (3) fiber lengths of BF white matter projections. The tethering and fiber length maps were sign flipped such that maximum values on the scale reflect higher VAChT, lower tethering, and shorter fiber lengths. The highest convergence of these three features selectively colocalizes midcingulo-insular hubs of the ventral attention network (white boundaries derived from Yeo et al.35). B Depending on the subregional point of origin within the BF (anteromedial or posterolateral) and cortical target, BF cholinergic neurons may exhibit either a modular (more neurons, fewer branches) or diffuse (fewer neurons, more branches) profile of arborization.