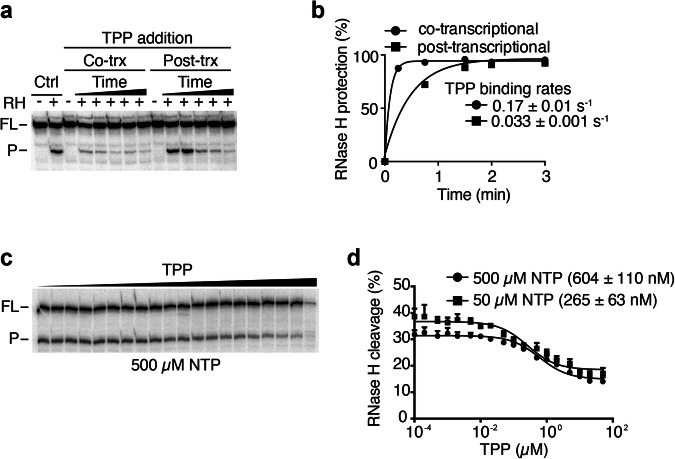
Fig. 3. TPP sensing is preferentially achieved cotranscriptionally by the tbpA riboswitch.
a RNase H probing experiments monitoring TPP binding when performed cotranscriptionally (Co-trx) or post-transcriptionally (Post-trx). Control reactions (Ctrl) done in the presence of RNase H (RH) show a cleaved product (P) and the uncleaved full-length (FL) transcript without TPP. Cotranscriptional binding was determined by adding TPP before transcription initiation and performing RNase H cleavage during transcription. Post-transcriptional measurements were achieved by performing transcription without TPP, which was followed by the addition of rifampicin, TPP and RNase H cleavage assays. b Quantifications of cotranscriptional and post-transcriptional binding assays. Experiments were fitted to a single-exponential assays and the values of the calculated rates are indicated. c Kswitch measurements for the wild-type tbpA riboswitch done in the presence of increasing TPP concentrations. The full-length (FL) and the cleave product (P) are shown on the left of the gel. d Quantification of the Kswitch experiments done when using 50 µM or 500 µM NTP. The Kswitch value is increasing upon decreasing the NTP concentrations. The average and the standard deviations are shown for each data point.