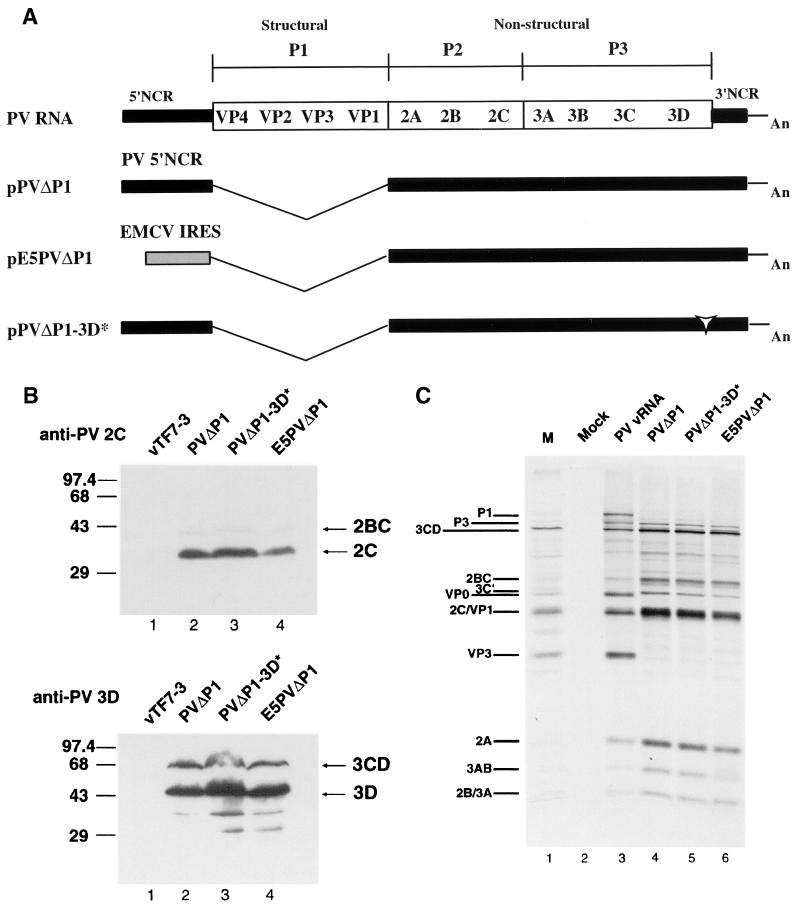
FIG. 1.
(A) Schematic representation of full-length and subgenomic PV RNAs used in this study. PVΔP1 and PVΔP1-3D∗ RNAs contain two nonviral guanylate residues at the 5′ ends of the RNAs transcribed by T7 RNA polymerase. Black bars denote PV sequences; the gray box denotes the EMCV IRES sequence in E5PVΔP1 RNA; the open arrowhead indicates insertion of the codon for Ile in PVΔP1-3D∗; An represents the 30-mer poly(A) tail. (B) Immunoblot analysis of HeLa cells expressing PV proteins. HeLa cells were infected with vTF7-3 and simultaneously transfected with pPVΔP1 (lane 2), pPVΔP1-3D∗ (lane 3), or pE5PVΔP1 (lane 4). Cells were harvested 14 hs after transfection and subjected to sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and Western immunoblotting with rabbit anti-PV2C serum (top) or rabbit anti-PV3D serum (bottom). Cells infected with vTF7-3 and mock transfected are shown in lane 1. In all lanes, extracts from approximately 5 × 104 cells were loaded. Positions of 2C, 2BC, 3D, and 3CD (right) and protein markers (left, in kilodaltons) are indicated. (C) In vitro translation of subgenomic RNAs. HeLa cell-free translation reactions were programmed with PV RNA (lane 3) or the indicated subgenomic RNAs transcribed in vitro (lanes 4 to 6). The identities of PV proteins are indicated. Lane 1, marker (M) PV proteins produced in infected cells; lane 2, no RNA.