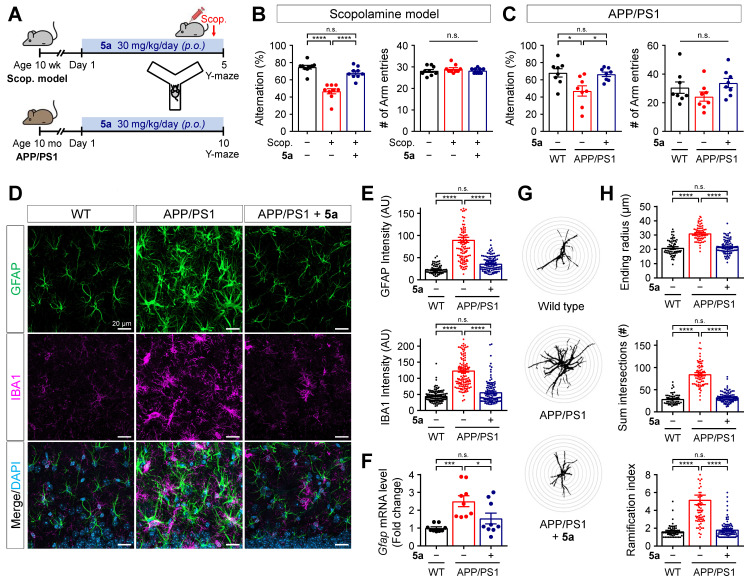
Figure 6.
5a ameliorates cognitive impairment and AD-like features in mice with AD. (A) Experimental protocol for the Y-maze test after oral administration of 5a in mice with scopolamine-induced cognitive impairment (n = 9 mice per group) or APP/PS1 mice (n = 8 mice per group). (B-C) Percentage of spontaneous alternations (left) and number of arm entries (right) for mice with scopolamine-induced cognitive impairment (B) or APP/PS1 mice (C) treated with vehicle or 5a in the Y-maze test. (D) Representative immunofluorescence images showing GFAP (green) and IBA1 (magenta) in the hippocampal dentate gyrus of WT and APP/PS1 mice treated with vehicle or 5a (n = 8 brain sections from four mice per group). (E) Quantification of immunoreactivity for GFAP (top) and IBA1 (bottom) in (D). (F) Relative mRNA expression of Gfap in the hippocampus of WT and APP/PS1 mice treated with vehicle or 5a (n = 9 mice per group). Hprt mRNA levels were used to normalize Gfap expression. (G) Representative images of Sholl analysis for GFAP-positive astrocytes in the hippocampal dentate gyrus of WT and APP/PS1 mice treated with vehicle or 5a (n = 59-90 astrocytes in 8 brain sections from four mice per group). Interval of concentric circles, 3.125 μm. (H) Quantification of ending radius (top), sum of intersections (middle), and ramification index (bottom) of GFAP-positive astrocytes by Sholl analysis. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001 and ****P < 0.0001; n.s., not significant (one-way ANOVA with Tukey's test). Data are presented as mean ± SEM. Scop.: scopolamine; AU: arbitrary unit.