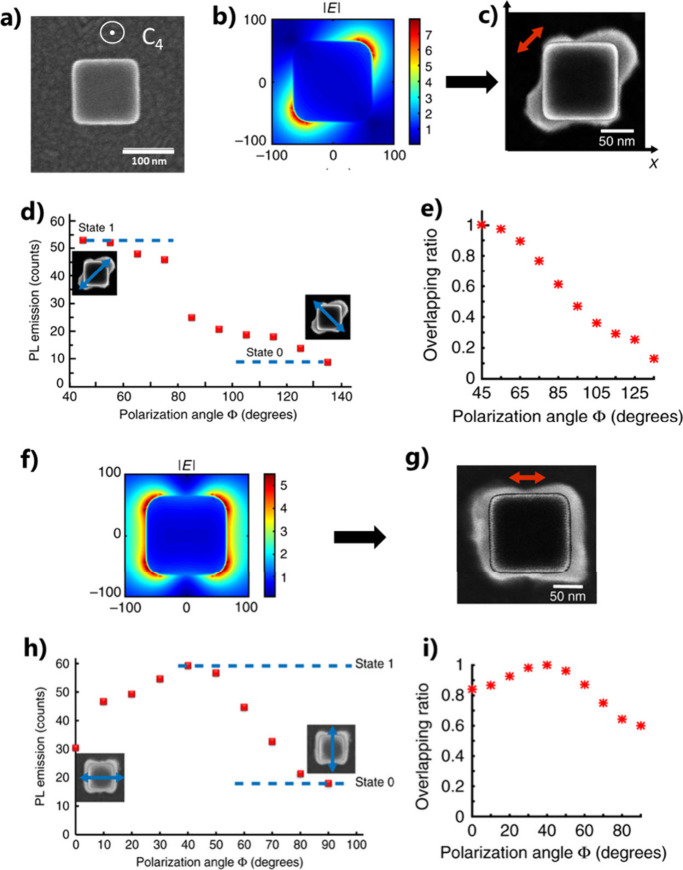
Figure 13.
D4h symmetry of a gold nanocube leads to D2h or D4h symmetry of the active medium by P2PP using linear polarization. (a) SEM image of a gold nanocube. (b) FDTD calculation of the plasmonic near-field amplitude of the nanocube at λ = 780 nm. The incident polarization is along one of the diagonals of the cube’s top square (dipolar plasmonic eigenmode). (c) SEM image of the resulting HPN: the Au nanocube is surrounded by two polymer lobes containing QDs, oriented along one of the diagonals of the cube’s top square. The red arrow represents the direction of polarization used for P2PP. The plasmonic field is molded by the P2PP photopolymer. (d) Photoluminescence intensity from the hybrid structure in (c) as a function of ϕ, the angle of polarization of the exciting linearly polarized laser beam at 405 nm wavelength. (e) Corresponding calculated overlap ratio defined in eq 8. (f) FDTD calculation of the plasmonic near-field amplitude of a 100 nm edge nanocube at λ = 780 nm for an incident polarization parallel to one of the nanocube’s edge. (g) SEM image of the resulting HPN: the Au nanocube is surrounded by polymer, containing QDs, presenting a D4h symmetry. The red arrow represents the direction of polarization used for P2PP. (h) Photoluminescence intensity from the hybrid structure in (g) as a function of ϕ, the angle of polarization of the exciting linearly polarized laser beam at 405 nm wavelength. (i) The corresponding calculated overlap factor defined in eq 8. (a–c,f–i) Adapted with permission from ref (3). Copyright 2020 The Author(s) under Creative Commons CC BY license.