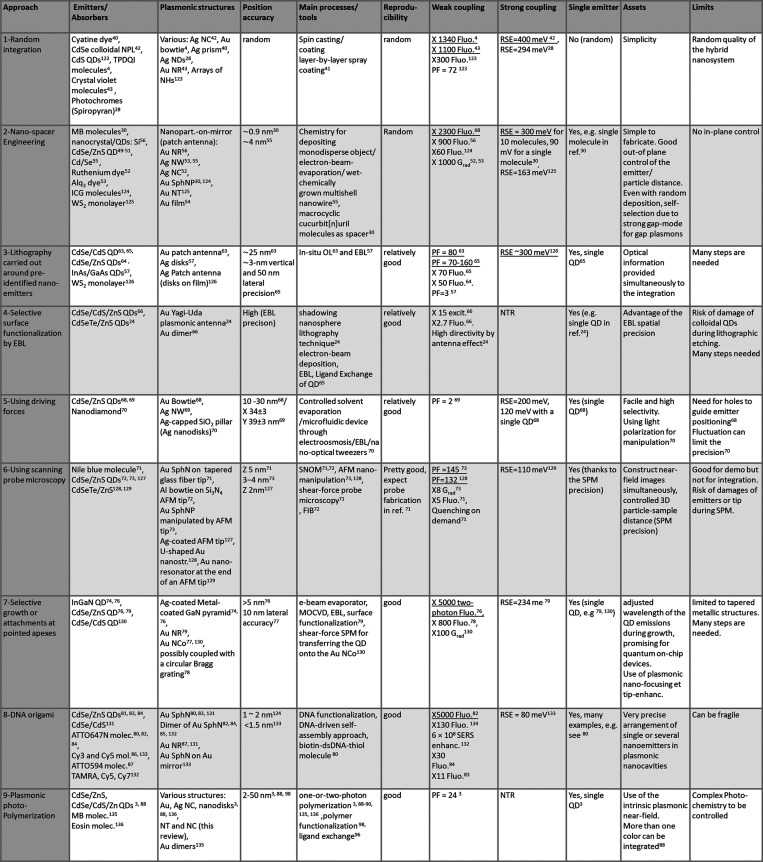
Figure 16.
Summary of the nine different approaches (and associated features and stated achievements) used for controlling the spatial localization on nanoemitters/absorbers in hybrid plasmonic nanosystems. Examples of the corresponding references are given. In order to complete the review, references(123−136), not cited in the manuscript, have been added. The highest values reported for fluorescence intensity enhancement, Purcell factor, and Rabi splitting energy are highlighted with underline. Acronyms used: AFM: Atomic Force Miscroscopy; Alq3: tris(8-hydroxyquinoline) aluminum; Enhanc.: enhancement; FIB: Focused Ion Beam; Fluo.: Fluorescence intensity; EBL: ebeam lithography; Enhanc.: enhancement. MB: methylene blue; MOCVD: Metal–Organic Chemical Vapor Deposition; Molec.: Molecule; Nanostr: nanostructure; Nanopart.: nanoparticle; NC: nano cube; NCo: nano cone; ND: nano disk; NH: nano hole; NR: nanorod; NPL nanoplatelets; NT: nano triangle; NTR: nothing to report; OL: optical lithography; PF: Purcell Factor; polymeriz.: polymerization; QD: quantum dot; RSE: Rabi splitting energy; SphNP: spherical nanoparticle, SPM: scanning probe microscopy; TAMRA: Carboxytetramethylrhodamine; TPDDI: N,N0-bis(2,6-diisopropylphenyl)-1,6,11,16-tetra-[4(1,1,3,3-tetramethylbutyl)phenoxy]quaterrylene-3,4:13,14-bis(dicarboximide).