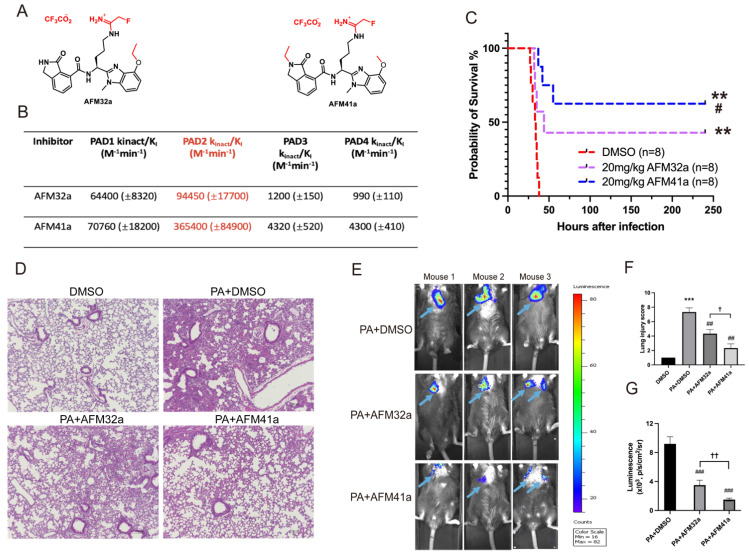
Figure 1.
PAD2 inhibitors decreased susceptibility and mortality against Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PA) infection. (A-B) Structures and Kinct/KI values for PAD2 inhibitors AFM32a and AFM41a. (C) WT mice were intranasally challenged with 2.5×106 CFU PA 19660/mouse and subsequently administered a single dose of AFM32a (20 mg/kg of body weight) or AFM41a (20 mg/kg of body weight) or an equivalent dose of DMSO 0.5 hours after infection. Survival rates were monitored for 10 days (n=8/group), and analysis was conducted using Mantel-Cox test. (D) Lung tissue samples were collected 24 hours after PA infection and subjected to H&E staining. (E) Whole animal imaging of bioluminescence was obtained using IVIS XRII system 24 hours after mice challenged with 2.5×106 CFU PA Xen-41/mouse (arrows indicating PA spread regions). (F) Lung injury scores. (G) Quantitative analysis of bioluminescence. *p<0.05 vs DMSO; **p<0.01 vs DMSO; ***p<0.001 vs DMSO; #p<0.05 vs 20mg/kg AFM32a; ##p<0.01 vs PA+AFM32a; ✚ p<0.05 vs PA+AFM32a.