Figure 6. An mRNA prime followed by an mRNA boost generates a long-lasting HIV humoral immune response.
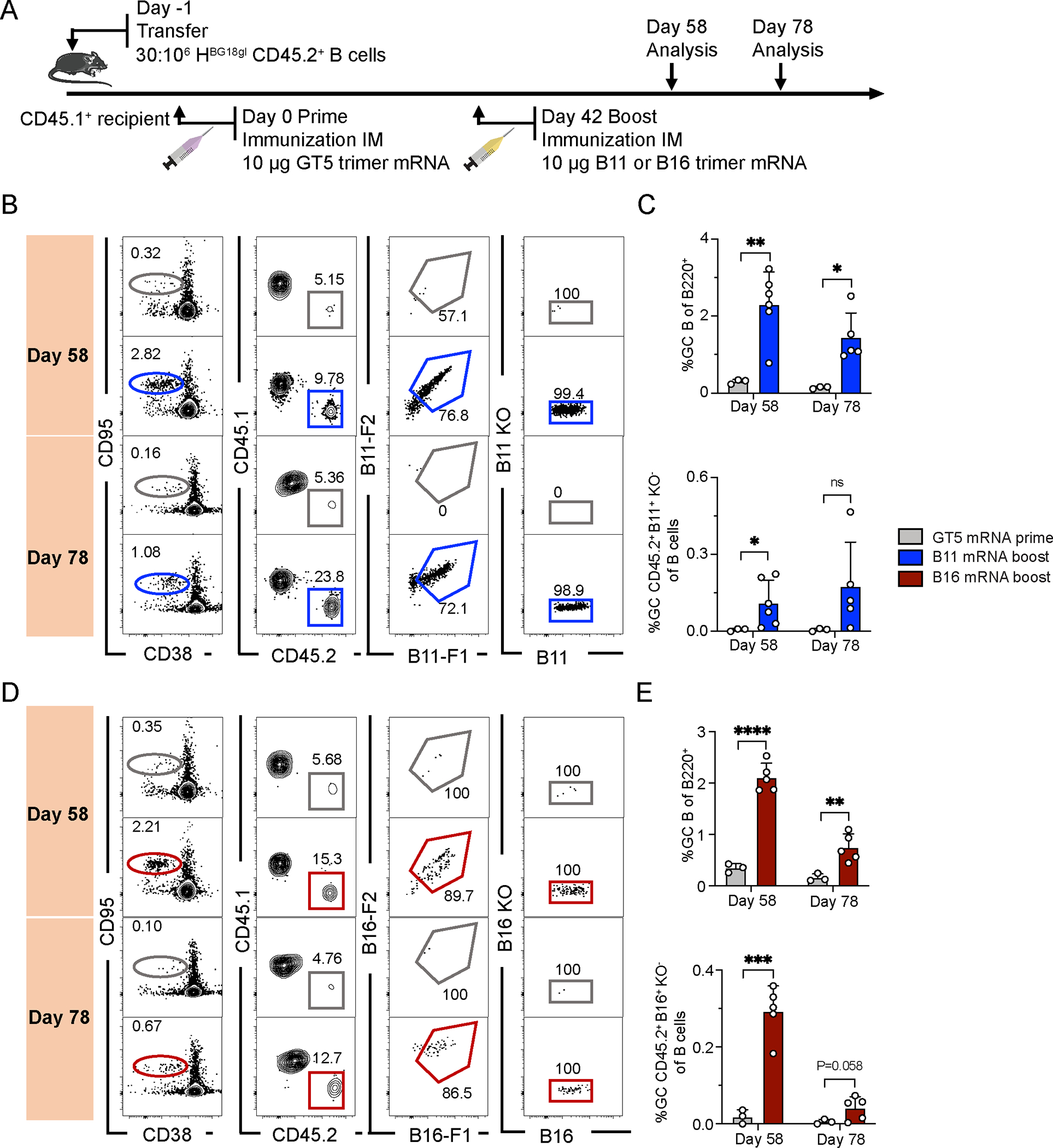
(A) Schematic of BG18gH B cell adoptive transfer recipients primed with GT5 mRNA on day 0, followed by boosting with B11 and B16 mRNA on day 42. Samples were collected on days 58 and 78 for analysis. Data was collected from one experiment. (B) Gating strategy for GC, CD45.2 cells in GC, B11-binders of CD45.2 cells in GC and epitope-binding specificity. (C) Quantification of GC size and B11-specific CD45.2+ GC B cell binders in total B cells. Each symbol represents a different mouse: BG18gH (GT5 mRNA prime), n=3; BG18gH (B11 mRNA boost), n=5 or 6. (D) Gating strategy for GC, CD45.2 cell in GC, B16 binders of CD45.2+ cells in GC and epitope-binding specificity. (E) Quantification of GC size and B16 specific CD45.2+ GC B cell binders in total B cells. Each symbol represents a different mouse: BG18gH (GT5 mRNA prime), n=3; BG18gH (B16 mRNA boost), n=5. Multiple t-tests without consistent SD assumptions used in C and E. Bars represent mean + SD, nsp >0.05, *p <0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.
