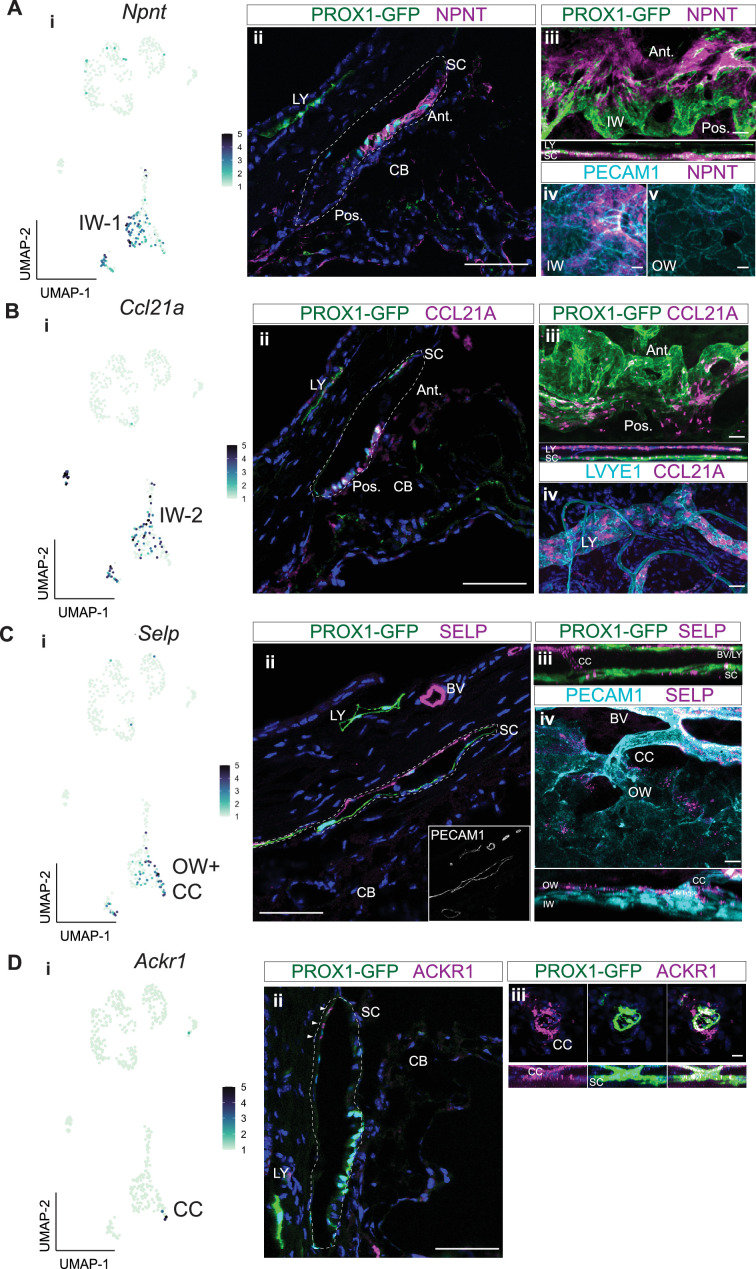
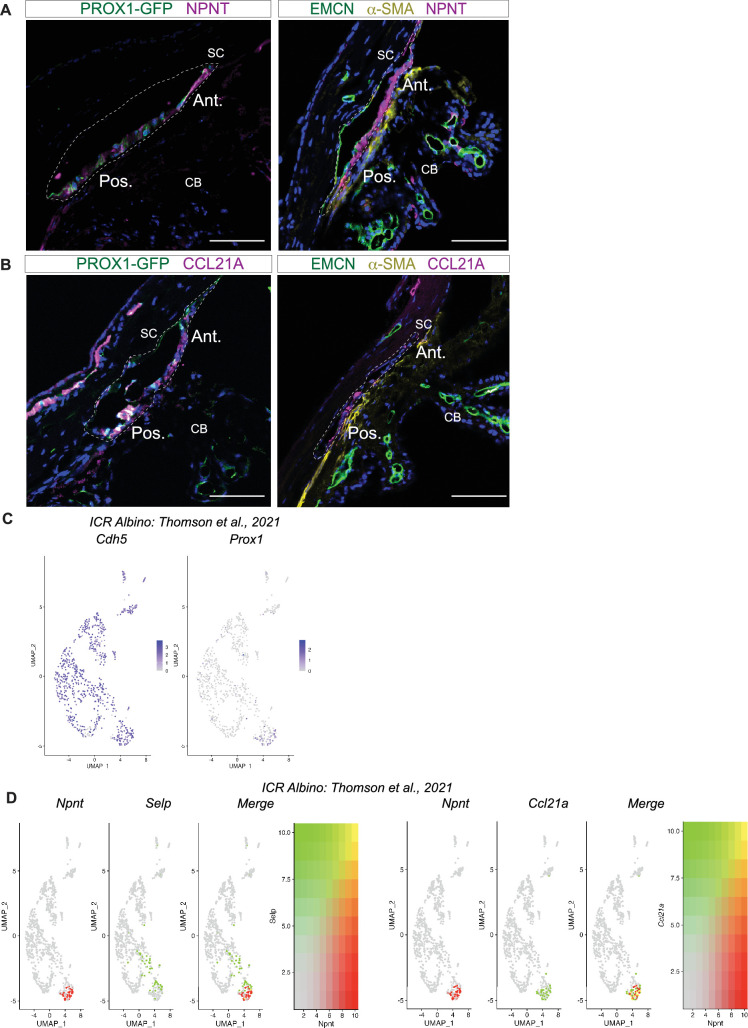
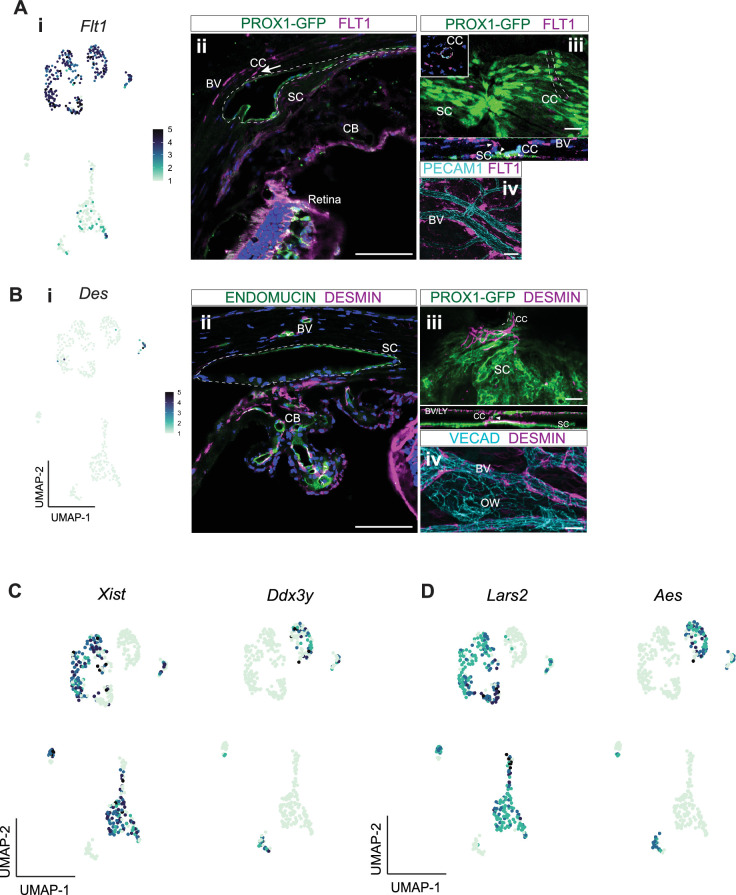
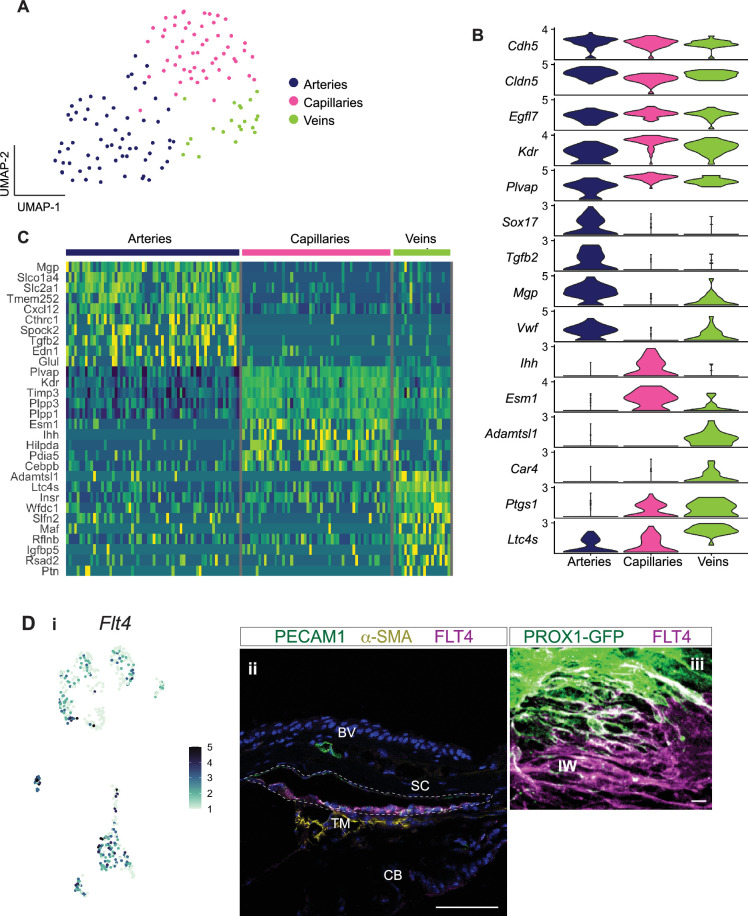
Figure 5. Immunofluorescence validates cell types and discovers bias for discrete localization of IW1 and IW2 cells.
(A) Npnt expression in a subgroup of SEC in scRNA-seq data (i) and corresponding immunofluorescence (IF) reveals high level of expression of NPNT in anterior portion of IW of SC in a frozen section (ii) and whole mount (iii and iv). (B) Ccl21a is expressed in SECs and LECs (i) and corresponding IF reveals high expression in posterior portion of IW of SC in a frozen section (ii) and whole mount (iii and iv). (C) Selp is expressed in OW SECs and CCs, a subgroup of SECs in single-cell (i) and corresponding IF (ii frozen section, iii-iv whole mount). (D) Ackr1 expression in a subset of CC cells (i) and corresponding IF (ii frozen section, iii whole mount). DAPI in blue labels nuclei in all panels. IW: Inner wall, OW: Outer wall, CC: Collector channels, CB: Ciliary body, LY: Lymphatic vessels, BV: Blood vessels SC: Schlemm’s canal. Ant.: Anterior SC, Post.: Posterior SC. Scale bar = 100μm.