Abstract
Five lipoproteins of sheep serum expressing A-esterase activity, but with differing activities towards four organophosphate substrates, were separated by a combination of gel filtration and ion-exchange chromatography. Each had an Mr of approx. 360,000 and contained a major peptide of Mr 28,000-30,000 that appeared to be present as several isoforms on urea/agarose isoelectric focusing. In every case this peptide split into a number of bands on urea/agarose isoelectric focusing. The bands appear to represent isoforms of the peptide, and four lipoproteins yielded characteristic patterns of bands. This peptide resembles the apolipoprotein A-I of human serum, and available evidence suggests that this is the protein that expresses A-esterase activity. Evidence is presented for the existence of different species of high-density lipoprotein HDL2 particles containing different complements of peptide isoforms and expressing contrasting substrate specificities towards organophosphates.
Full text
PDF

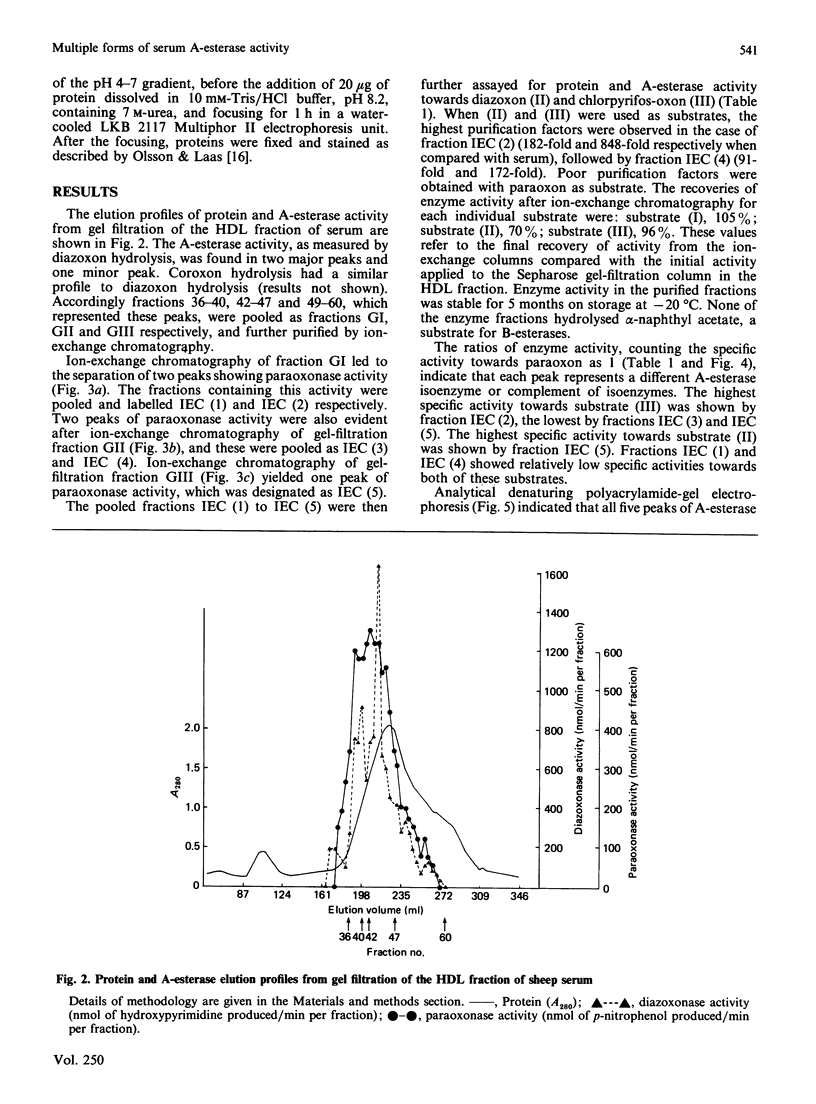
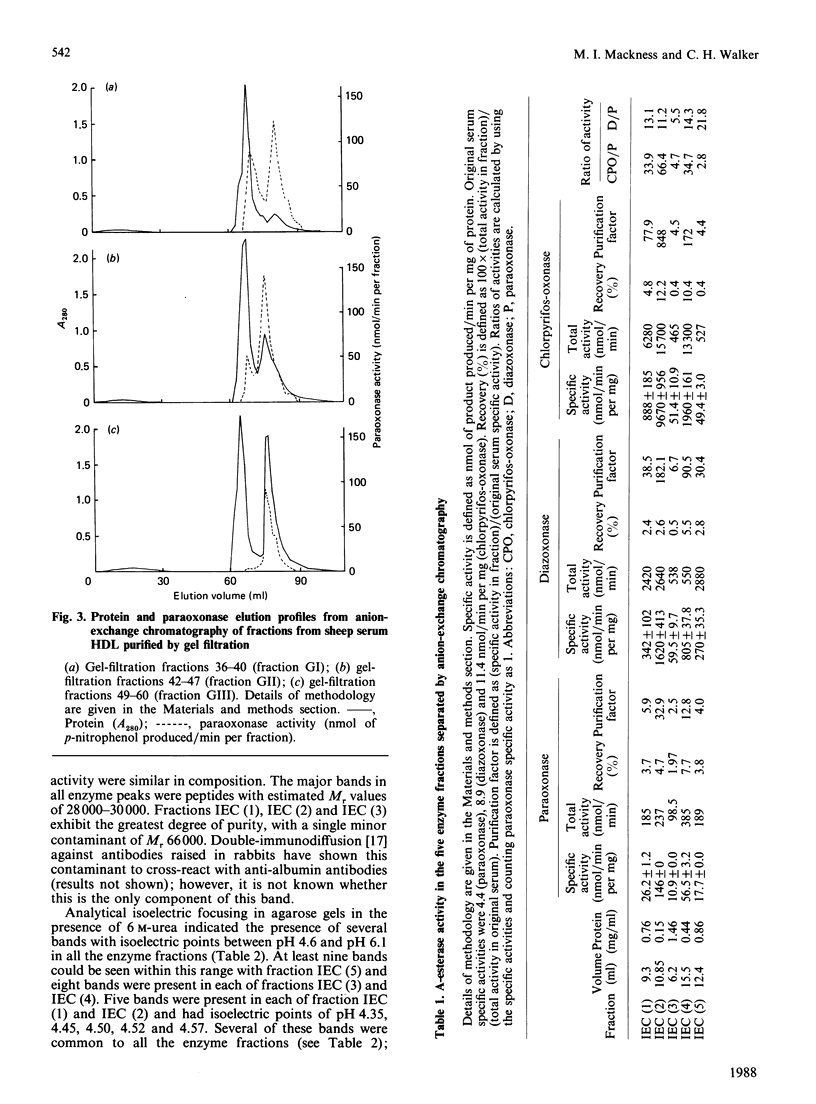
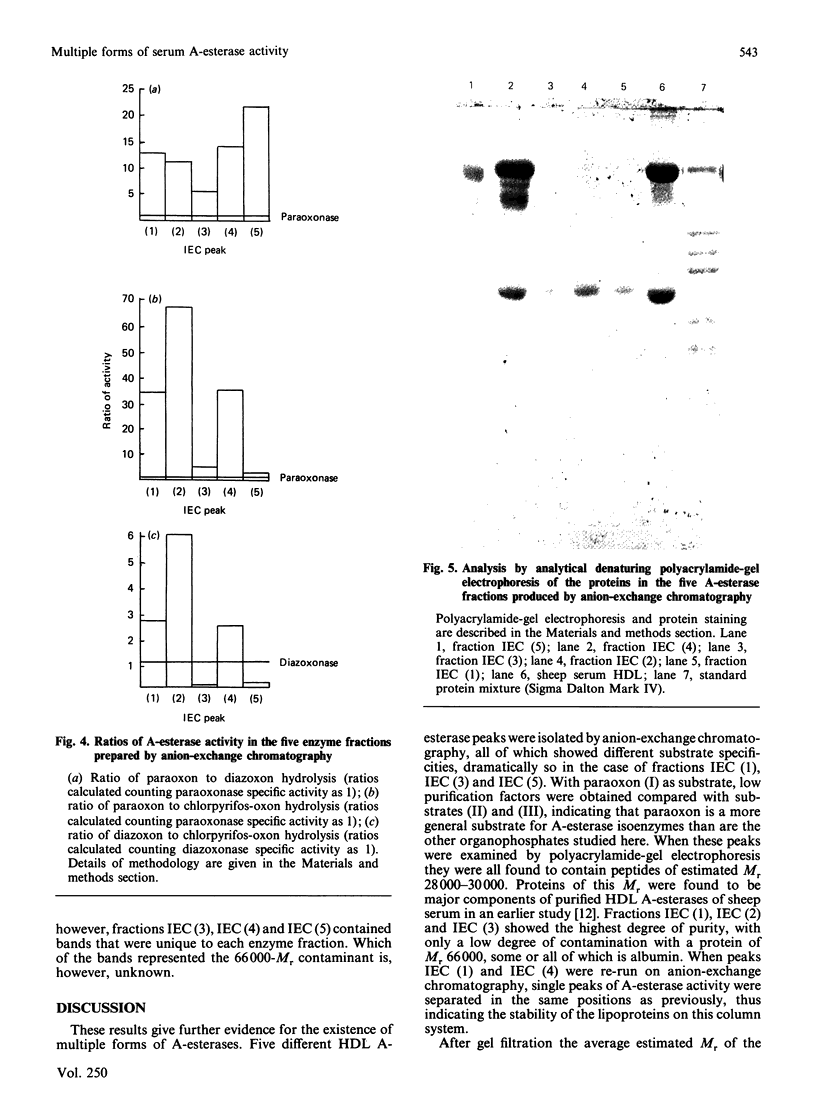


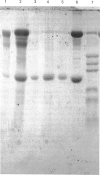
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALDRIDGE W. N. Serum esterases. I. Two types of esterase (A and B) hydrolysing p-nitrophenyl acetate, propionate and butyrate, and a method for their determination. Biochem J. 1953 Jan;53(1):110–117. doi: 10.1042/bj0530110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALDRIDGE W. N. Serum esterases. II. An enzyme hydrolysing diethyl p-nitrophenyl phosphate (E600) and its identity with the A-esterase of mammalian sera. Biochem J. 1953 Jan;53(1):117–124. doi: 10.1042/bj0530117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albers J. J., Albers L. V., Aladjem F. Isoelectric heteogeneity of the major polypeptide of human serum high density lipoproteins. Biochem Med. 1971 Feb;5(1):48–55. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(71)90074-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. W., Nichols A. V., Forte T. M., Lindgren F. T. Particle distribution of human serum high density lipoproteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jul 22;493(1):55–68. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(77)90259-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker H. N., Delahunty T., Gotto A. M., Jr, Jackson R. L. The primary structure of high density apolipoprotein-glutamine-I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3631–3634. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brealey C. J., Lawrence D. K. High-performance liquid chromatography of pirimiphos methyl and five metabolites. J Chromatogr. 1979 Jan 21;168(2):461–469. doi: 10.1016/0021-9673(79)80017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiberg H., Mohr J., Schmiegelow K., Nielsen L. S., Williamson R. Linkage relationships of paraoxonase (PON) with other markers: indication of PON-cystic fibrosis synteny. Clin Genet. 1985 Oct;28(4):265–271. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1985.tb00400.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostner G. M., Holasek A. The separation of human serum high density lipoproteins by hydroxy apatite column chromatography. Evidence for the presence of discrete subfractions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Sep 28;488(3):417–431. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(77)90200-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackness M. I., Hallam S. D., Peard T., Warner S., Walker C. H. The separation of sheep and human serum "A"-esterase activity into the lipoprotein fraction by ultracentrifugation. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1985;82(4):675–677. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(85)90506-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackness M. I., Thompson H. M., Hardy A. R., Walker C. H. Distinction between 'A'-esterases and arylesterases. Implications for esterase classification. Biochem J. 1987 Jul 1;245(1):293–296. doi: 10.1042/bj2450293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackness M. I., Walker C. H., Carlson L. A. Low A-esterase activity in serum of patients with fish-eye disease. Clin Chem. 1987 Apr;33(4):587–588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackness M. I., Walker C. H. Partial purification and properties of sheep serum "A'-esterases. Biochem Pharmacol. 1983 Aug 1;32(15):2291–2296. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(83)90175-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcel Y. L., Weech P. K., Nguyen T. D., Milne R. W., McConathy W. J. Apolipoproteins as the basis for heterogeneity in high-density lipoprotein2 and high-density lipoprotein3. Studies by isoelectric focusing on agarose films. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Sep 17;143(3):467–476. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08394.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McElveen J., Mackness M. I., Colley C. M., Peard T., Warner S., Walker C. H. Distribution of paraoxon hydrolytic activity in the serum of patients after myocardial infarction. Clin Chem. 1986 Apr;32(4):671–673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mentlein R., Berge R. K., Heymann E. Identity of purified monoacylglycerol lipase, palmitoyl-CoA hydrolase and aspirin-metabolizing carboxylesterase from rat liver microsomal fractions. A comparative study with enzymes purified in different laboratories. Biochem J. 1985 Dec 1;232(2):479–483. doi: 10.1042/bj2320479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mentlein R., Heiland S., Heymann E. Simultaneous purification and comparative characterization of six serine hydrolases from rat liver microsomes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 Apr 1;200(2):547–559. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90386-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mentlein R., Heymann E. Hydrolysis of ester- and amide-type drugs by the purified isoenzymes of nonspecific carboxylesterase from rat liver. Biochem Pharmacol. 1984 Apr 15;33(8):1243–1248. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(84)90176-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nestruck A. C., Suzue G., Marcel Y. L. Studies on the polymorphism of human apolipoprotein A-I. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jan 18;617(1):110–121. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(80)90228-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesch F., Timms C. W., Walker C. H., Guenthner T. M., Sparrow A., Watabe T., Wolf C. R. Existence of multiple forms of microsomal epoxide hydrolases with radically different substrate specificities. Carcinogenesis. 1984 Jan;5(1):7–9. doi: 10.1093/carcin/5.1.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmiegelow K., Eiberg H., Tsui L. C., Buchwald M., Phelan P. D., Williamson R., Warwick W., Niebuhr E., Mohr J., Schwartz M. Linkage between the loci for cystic fibrosis and paraoxonase. Clin Genet. 1986 May;29(5):374–377. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1986.tb00507.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theodor J. L. Distinction between "self" and "not-self" in lower invertebrates. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):690–692. doi: 10.1038/227690a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitello L. B., Scanu A. M. Studies on human serum high density lipoproteins. Self-association of apolipoprotein A-I in aqueous solutions. J Biol Chem. 1976 Feb 25;251(4):1131–1136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama S., Tajima S., Yamamoto A. The process of dissolving apolipoprotein A-I in an aqueous buffer. J Biochem. 1982 Apr;91(4):1267–1272. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]