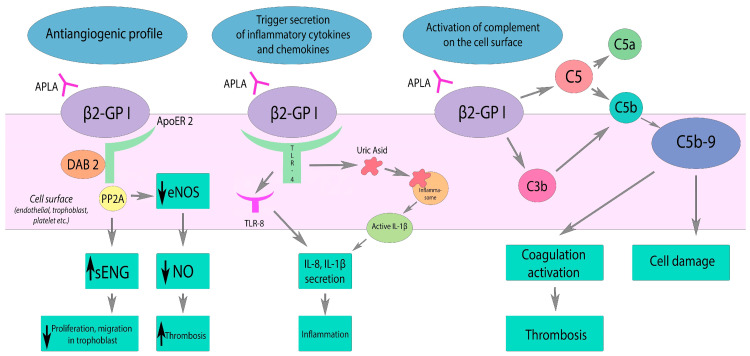
Figure 1. Effects of aPLA on the complement system, inflammation, and vascular tone. Black arrows indicate the direction of change: downward for a decrease and upward for an increase [6].
aPLA diminishes eNOS activity through its interaction with ApoER2, resulting in decreased NO production. This reduction in NO leads to impaired vasodilation and endothelial dysfunction. Additionally, aPLA triggers the activation of TLR and inflammasome pathways, promoting the release of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines. On the cell surface, aPLA also activates the complement system, culminating in coagulation activation and cell damage due to C5b-9 deposition.
β2GPI: Beta-2-glycoprotein I, ApoER2: Apolipoprotein E2 receptor; DAB2: Disabled-2; PP2A: Protein phosphatase 2A; eNOS: Nitric oxide synthase; sENG: Soluble endoglin; TLR: Toll-like receptor; TLT-8: Toll-like receptor 8; aPLA: Antiphospholipid antibodies; NO: Nitric oxide