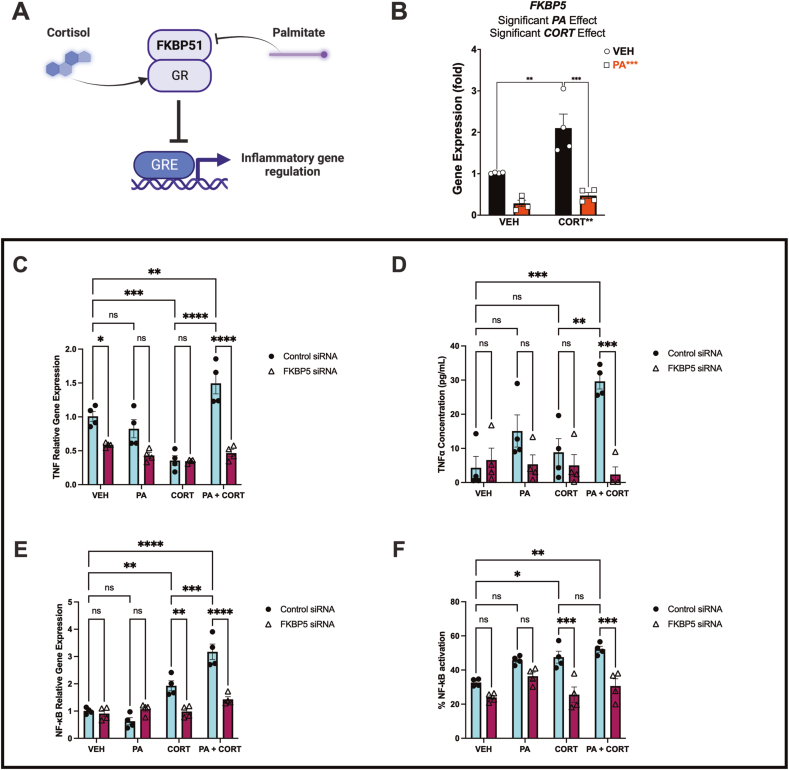
Fig. 10.
Human FKBP5 regulates microglial TNF-α levels under obesogenic factors. (A) Schematic model illustrating the primary hypothesis that PA disrupts pro-inflammatory gene expression mediated by the glucocorticoid receptor (GR) through FKBP5/FKBP51 regulation. (B) In support of this notion, PA significantly reduced FKBP5 mRNA levels (p < 0.0001)—sample size = four independent experiments. FKBP5 siRNA delivery attenuated the impact of PA + CORT on TNF-α upregulation (p < 0.0001) (C) and released protein levels of TNF-α (p = 0.0001) (D). CORT increased NF-κB gene expression (E) and protein activation (p < 0.05) (F). This effect was reduced in cells treated with FKBP5 siRNA (p < 0.001) (E-F)—sample size = four independent experiments.