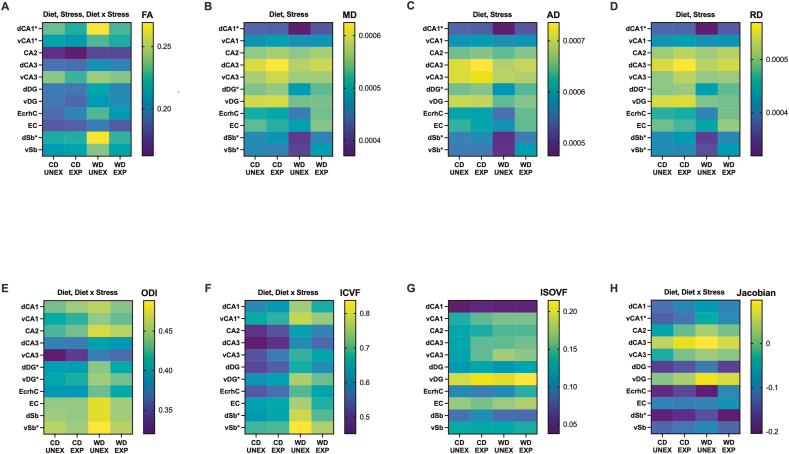
Fig. 3.
Exposure to an obesogenic environment during adolescence impacts the structural integrity of distinctive hippocampal subfields, subregions, and adjacent areas. Heatmaps of hippocampal structural changes based on each diffusion-MRI parameter value. (A) Fractional anisotropy (FA) was significantly modified by the WD (p < 0.0001), PSS (p = 0.0022), and the interactions between WD and PSS (p = 0.022). (B–D) Medial (MD), axial (AD), and radial diffusivity (RD) were also significantly altered by the WD (MD, p = 0.030; AD, p = 0.036; RD, p = 0.028) and PSS (MD, p = 0.030; AD, p = 0.033; RD, p = 0.030). (E–H) Orientation dispersion index (ODI), intracellular volume fraction (ICVF), and Jacobian lob matrix data derived from DTI/NODDI analysis revealed that the WD (ODI, p < 0.0001; ICVF, p < 0.0001; Jacobian, p = 0.0023), and WD x PSS (p = 0.0131) (p = 0.0057) (p = 0.0270) significantly contributed to changes in hippocampal tissue integrity. (G) The isotropic volume fraction remained unaffected by the experimental conditions. This indicates that changes observed in other DTI metrics are not due to alterations in the overall isotropic volume but may instead reflect changes in tissue microstructure or organization. Asterisks indicate region-specific post hoc effects that significantly contribute to the main and interaction effects observed in the two-way ANOVA (FA: dCA1, vCA1; MD: dCA1, dDG, vSb; AD: dCA1, dDG, dSb, vSb; RD: dCA1, dDG, vSb; ODI: dDG, vDG, vSb; ICVF: vCA1, vDG, dSb, vSb, Jabobian: vCA1, dSb). Sample numbers: CD UNEXP, n = 6; CD EXP, n = 7; WD UNEXP, n = 8, WD EXP; n = 7. Abbreviations: d, dorsal; v, ventral; CA, Cornu Ammonis, DG, dentate gyrus, EcrhC, ectorhinal cortex; EC, entorhinal cortex; Sb, subiculum; CD, control diet; WD, Western-like diet; UNEX, unexposed; EXP, PSS exposed.