Table 2.
Model description after Nordlie et al. (2009).
| Model summary | |
| Populations | 34 areas (Table 1) with a total of 254 populations. The model consists of about 3.5 million neurons and 43 billion synapses. |
| Geometry | — |
| Connectivity | area- and population-specific but otherwise random |
| Neuron model | LIF, fixed absolute refractory period (voltage clamp) |
| Synapse model | exponential postsynaptic currents |
| Plasticity | — |
| Input | independent homogeneous Poisson spike trains |
| Measurements | spiking activity |
| Populations | |
| Type | Cortex |
| Elements | LIF neurons |
| Number of populations | 34 areas with 8 populations each (areas caudalanteriorcingulate, caudalmiddlefrontal, entorhinal, lateraloccipital, parsorbitalis, precentral, rostralanteriorcingulate have 6, and the parahippocampal area has 4), 2 per layer |
| Population size |
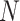 (area- and population-specific)
(area- and population-specific) |
| Connectivity | |
| Type | source and target neurons drawn randomly with replacement (allowing autapses and multapses) with area- and population-specific connection probabilities. The total number of synapses between populations is fixed, corresponding to the “Random, fixed total number” rule described by Senk et al. (2022). |
| Weights | fixed, drawn from normal distribution with mean 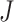 such that postsynaptic potentials have a mean amplitude of such that postsynaptic potentials have a mean amplitude of 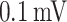 and standard deviation and standard deviation 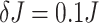 ; 4E to 2/3E increased by factor ; 4E to 2/3E increased by factor 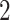 (cf. Potjans and Diesmann 2014); weights of inhibitory connections increased by factor (cf. Potjans and Diesmann 2014); weights of inhibitory connections increased by factor 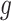 ; excitatory weights ; excitatory weights 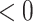 and inhibitory weights and inhibitory weights 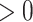 are redrawn; inter-areal weights onto inhibitory populations increased by factor are redrawn; inter-areal weights onto inhibitory populations increased by factor 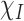 and onto excitatory and inhibitory populations increased by factor and onto excitatory and inhibitory populations increased by factor 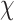
|
| Delays | fixed, drawn from truncated lognormal distribution with mean 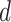 and standard deviation and standard deviation 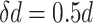 ; delays of inhibitory connections factor ; delays of inhibitory connections factor 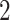 smaller; delays rounded to the nearest multiple of the simulation step size smaller; delays rounded to the nearest multiple of the simulation step size 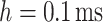 , inter-area delays drawn from a truncated lognormal distribution with mean , inter-area delays drawn from a truncated lognormal distribution with mean 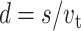 , with distance , with distance 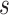 and average transmission speed and average transmission speed 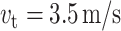 (Girard et al. 2001); and standard deviation (Girard et al. 2001); and standard deviation 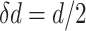 , distances determined as the median of the distances between all vertex pairs of the 2 areas in the DTI data (Goulas et al. 2016), delays , distances determined as the median of the distances between all vertex pairs of the 2 areas in the DTI data (Goulas et al. 2016), delays 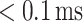 before rounding are redrawn before rounding are redrawn |
| Neuron and synapse model | |
| Name | LIF neuron |
| Type | LIF, exponential synaptic current inputs |
| Subthreshold dynamics |
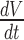
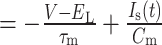 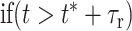 , , 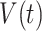 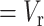 else, else, 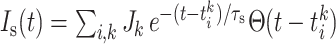 , , 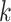 : neuron index, : neuron index, 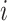 : spike index, : spike index, 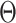 : Heaviside step function : Heaviside step function |
| Spiking | If 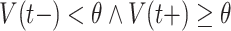 1. set 1. set 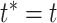 , 2. emit spike with time stamp , 2. emit spike with time stamp 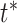
|
| Input | |
| Type | Background |
| Target | LIF neurons |
| Description | Independent homogeneous Poisson spike trains to all neurons in the network; rate fixed such that the mean input, measured relative to rheobase, is 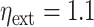
|
| Measurements | |
| Spiking activity | |
